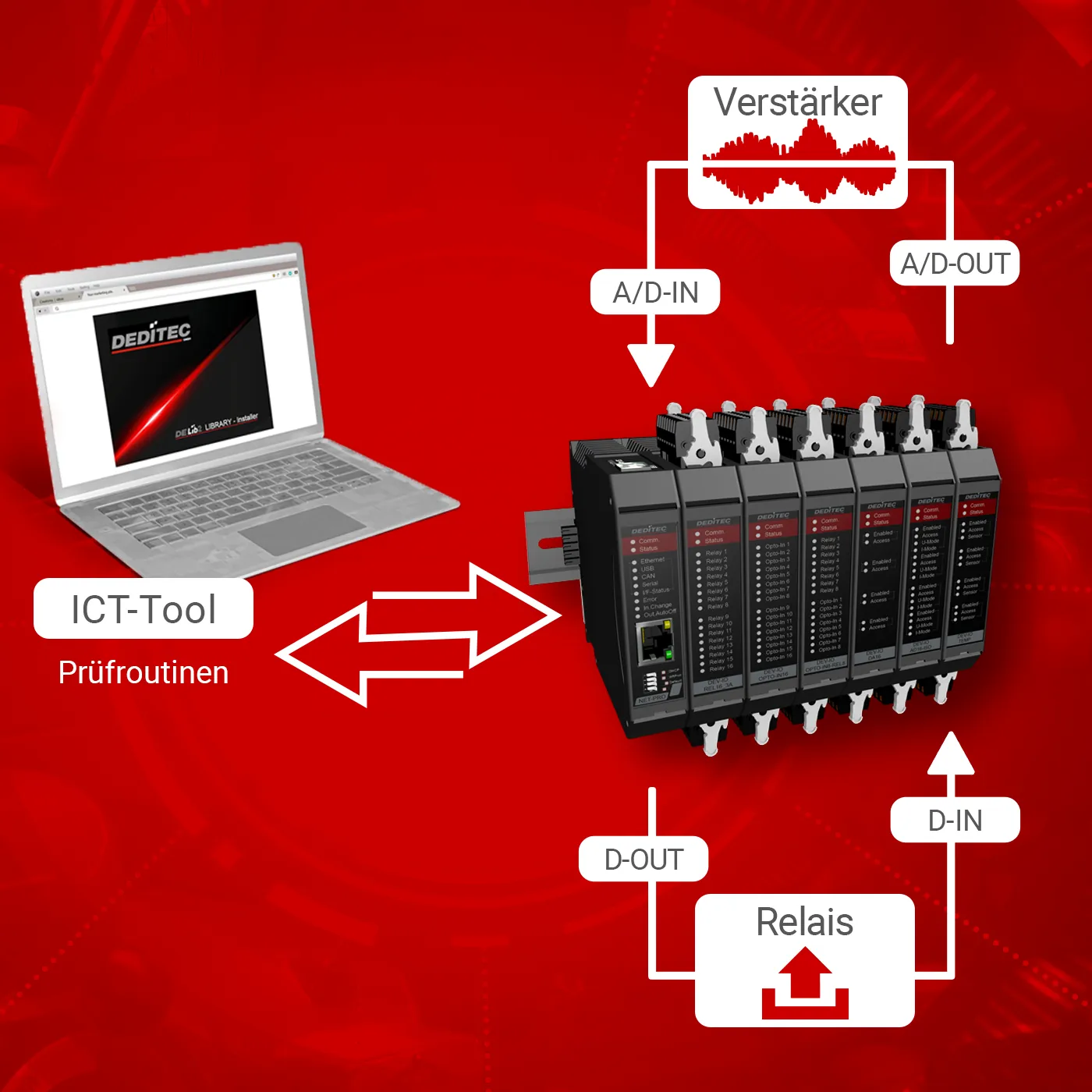
DELIB command overview
Here you will find an overview of all available DELIB commands, the support of which may vary depending on the product. A corresponding programming example illustrates the application.
Management functions
DapiOpenModule
This function opens a specific module.
Description
This function opens a specific module.
Definition
ULONG DapiOpenModule(ULONG moduleID, ULONG nr);
Parameter
moduleID=Specifies the module to be opened (see delib.h)
nr=Specifies which module is to be opened.
nr=0 -> 1. Module
nr=1 -> 2. Module
Return value
handle=Corresponding handle for the module
handle=0 -> Module was not found
Remark
The handle returned by this function is required to identify the module for all other functions.
Programming example
// Open USB module
handle = DapiOpenModule(RO_USB1, 0);
printf(„handle = %x\n“, handle);
if (handle==0)
{
// USB module was not found
printf(„Module could not be opened\n“);
return;
}
DapiCloseModule
This command closes an open module.
Description
This command closes an open module.
Definition
ULONG DapiCloseModule(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
None
Programming example
// Close module
DapiCloseModule(handle);
DapiGetDELIBVersion
This function returns the installed DELIB version.
Description
This function returns the installed DELIB version.
Definition
ULONG DapiGetDELIBVersion(ULONG mode, ULONG par);
Parameter
mode=Mode with which the version is read out (must always be 0).
par=This parameter is not defined (must always be 0).
Return value
version=Version number of the installed DELIB version [hex]
Programming example
version = DapiGetDELIBVersion(0, 0);
//With version 1.32 installed
version = 132(hex)
DapiSpecialCMDGetModuleConfig
This function returns the hardware configuration (number of input and output channels) of the module.
Description
This function returns the hardware configuration (number of input and output channels) of the module.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, par, 0, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Querying the number of digital input channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI
Query number of digital input flip-flops
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI_FF
Query number of digital input counters (16-bit counter)
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI_COUNTER
Query number of digital input counters (48-bit counter)
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_CNT48
Querying the number of digital output channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DO
Querying the number of digital pulse generator outputs
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_PULSE_GEN
Querying the number of digital PWM outputs
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_PWM_OUT
Querying the number of digital input/output channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DX
Querying the number of analog input channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_AD
Querying the number of analog output channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DA
Query number of temperature channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_TEMP
Query number of stepper channels
par=DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_STEPPER
Return value
Querying the number of digital input channels
return=number of digital input channels
Query number of digital input flip-flops
return=number of digital input flip-flops
Query number of digital input counters (16-bit counter)
return=number of digital input counters (16-bit counter)
Query number of digital input counters (48-bit counter)
return=number of digital input counters (48-bit counter)
Querying the number of digital output channels
return=number of digital output channels
Querying the number of digital pulse generator outputs
return=number of digital pulse generator outputs
Querying the number of digital PWM outputs
return=number of digital PWM outputs
Querying the number of digital input/output channels
return=number of digital input/output channels
Querying the number of analog input channels
return=number of analog input channels
Querying the number of analog output channels
return=number of analog output channels
Query number of temperature channels
return=number of temperature channels
Query number of stepper channels
return=number of stepper channels
Programming example
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of digital input channels
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DO, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of digital output channels
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DX, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of digital input/output channels
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_AD, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of analog input channels
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DA, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of analog output channels
ret=DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG,
DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_STEPPER, 0, 0);
//Returns the number of stepper channels
DapiOpenModuleEx
This function specifically opens a module with an Ethernet interface. The parameters IP address, port number and the duration of the timeout can be defined.
Description
This function specifically opens a module with an Ethernet interface. The parameters IP address, port number and the duration of the timeout can be defined. The module is opened independently of the settings made in the DELIB Configuration Utility.
Definition
ULONG DapiOpenModuleEx(ULONG moduleID, ULONG nr, unsigned char* exbuffer, 0);
Parameter
moduleID = Specifies the module to be opened (see delib.h)
nr = Specifies which module (if several) is to be opened.
nr = 0 -> 1. Module
nr = 1 -> 2. Module
exbuffer = Buffer for IP address, port number and duration of the timeout
Return value
handle = Corresponding handle for the module
handle = 0 -> Module was not found
Remark
The handle returned by this function is required to identify the module for all other functions.
This command is supported by all modules with an Ethernet interface.
Programming example
// Open ETH-Module with parameter
DAPI_OPENMODULEEX_STRUCT open_buffer;
strcpy((char*) open_buffer.address, "192.168.1.10");
open_buffer.portno = 0;
open_buffer.timeout = 5000;
handle = DapiOpenModuleEx(RO_ETH, 0, (unsigned char*) &open_buffer, 0);
printf("Module handle = %x\n", handle);
DapiScanAllModulesAvailable
This function can be used to scan all modules connected to the USB bus.
Description
This function can be used to scan all modules connected to the USB bus.
The module ID and module no. of each module found are determined.
Definition
ULONG DapiScanAllModulesAvailable(uint nr)
Parameter
nr = 0: All modules connected to the USB bus are searched for
nr = i: Reading out the individual connected modules
Return value
Indicates the number of modules found.
Programming example
no_of_modules =
DT.Delib.DapiScanAllModulesAvailable(0);
for (i = 1; i <= no_of_modules; i++)
{
ret = DapiScanAllModulesAvailable(i);
moduleID = ret & 0x0000ffff;
moduleNr = (ret >> 16) & 0xff;
}
Error handling
DapiGetLastError
This function returns the last error recorded.
Description
This function returns the last recorded error. If an error has occurred, it must be cleared with DapiClearLastError(), otherwise every call to DapiGetLastError() will return the "old" error.
If several modules are to be used, the use of DapiGetLastErrorByHandle() is recommended.
Definition
ULONG DapiGetLastError(void);
Parameter
None
Return value
Error code
0=no error. (see delib_error_codes.h)
Programming example
BOOL IsError()
{
unsigned char msg[500];
unsigned long error_code = DapiGetLastError();
if (error_code != DAPI_ERR_NONE)
{
DapiGetLastErrorText((unsigned char*) msg, sizeof(msg));
printf("Error Code = 0x%x * Message = %s\n", error_code, msg);
DapiClearLastError();
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
DapiGetLastErrorByHandle
This function returns the last error recorded for a specific module using the handle.
Description
This function returns the last error recorded for a specific module using the handle. If an error has occurred, it must be cleared with DapiClearLastErrorByHandle(), otherwise every call to DapiGetLastErrorByHandle() will return the "old" error.
Definition
ULONG DapiGetLastErrorByHandle(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
Error code
0=no error. (see delib_error_codes.h)
Programming example
BOOL IsError(ULONG handle)
{
unsigned long error_code = DapiGetLastErrorByHandle(handle);
if (error_code != DAPI_ERR_NONE)
{
printf("Error detected on handle 0x%x - Error Code = 0x%x\n", handle, error_code);
DapiClearLastErrorByHandle(handle);
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
DapiGetLastErrorText
This function reads out the text of the last error recorded.
Description
This function reads out the text of the last recorded error. If an error has occurred, it must be cleared with DapiClearLastError(), otherwise every call to DapiGetLastErrorText() will return the "old" error.
Definition
ULONG DapiGetLastErrorText(unsigned char * msg, unsigned long msg_length);
Parameter
msg = Buffer for the text to be received
msg_length = Length of the text buffer
Programming example
BOOL IsError()
{
unsigned char msg[500];
unsigned long error_code = DapiGetLastError();
if (error_code != DAPI_ERR_NONE)
{
DapiGetLastErrorText((unsigned char*) msg, sizeof(msg));
printf("Error Code = 0x%x * Message = %s\n", error_code, msg);
DapiClearLastError();
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
DapiClearLastError
This function deletes the last error that was recorded with DapiGetLastError().
Description
This function deletes the last error that was recorded with DapiGetLastError().
Definition
void DapiClearLastError(void);
Parameter
None
Return value
None
Programming example
BOOL IsError()
{
unsigned char msg[500];
unsigned long error_code = DapiGetLastError();
if (error_code != DAPI_ERR_NONE)
{
DapiGetLastErrorText((unsigned char*) msg, sizeof(msg));
printf("Error Code = 0x%x * Message = %s\n", error_code, msg);
DapiClearLastError();
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
DapiClearLastErrorByHandle
This function deletes the last error of a specific module (handle) that was recorded with DapiGetLastErrorByHandle().
Description
This function deletes the last error of a specific module (handle) that was registered with DapiGetLastErrorByHandle().
Definition
void DapiClearLastErrorByHandle(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
Return value
None
Programming example
BOOL IsError(ULONG handle)
{
unsigned long error_code = DapiGetLastErrorByHandle(handle);
if (error_code != DAPI_ERR_NONE)
{
printf("Error detected on handle 0x%x - Error Code = 0x%x\n", handle, error_code);
DapiClearLastErrorByHandle(handle);
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
Test functions
DapiPing
This command checks the connection to an open module.
Description
This command checks the connection to an open module.
Definition
ULONG DapiPing(ULONG handle, ULONG value);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
value=Transferred test value, in the value range of 0-255 (8-bit), to the module
Return value
The test value transferred with "value" must be returned here
Analog output functions
DapiDASetMode
This command sets the mode for a D/A converter.
Description
This command sets the mode for a D/A converter.
Definition
void DapiDASetMode(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG mode);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0 .. )
mode=Specifies the mode for the D/A converter
Return value
None
Remark
The following modes are supported:
(these depend on the D/A module used)
Unipolar voltages
ADDA_MODE_UNIPOL_10V
ADDA_MODE_UNIPOL_5V
ADDA_MODE_UNIPOL_2V5
Bipolar voltages
ADDA_MODE_BIPOL_10V
ADDA_MODE_BIPOL_5V
ADDA_MODE_BIPOL_2V5
Currents
ADDA_MODE_0_20mA
ADDA_MODE_4_20mA
ADDA_MODE_0_24mA
ADDA_MODE_0_25mA
ADDA_MODE_0_50mA
Programming example
// Sets channel 0 to 0 ... 10V mode
DapiDASetMode(handle, 0, DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_10V);
DapiDAGetMode
This command reads back the set mode of a D/A converter.
Description
This command reads back the set mode of a D/A converter.
Definition
ULONG DapiDAGetMode(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0 .. )
Return value
Mode of the D/A converter
Programming example
// Reads back the current mode of channel 1
unsigned long mode;
mode = DapiDAGetMode(handle, 0);
// Check mode
if(mode == DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_10V)
{
printf("Mode is 0 .. 10V");
}
DapiDASet
This command transfers a data value to a channel of a D/A converter.
Description
This command transfers a data value to a channel of a D/A converter.
Definition
void DapiDASet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0 .. )
data=Indicates the data value that is written
(16-bit data value -> data value range: 0-65535)
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiDASet(handle, 0, 65535);
// Sets the 1st output of the D/A converter to the maximum value of the selected mode.
selected mode.
//(if ADDA_MODE_UNIPOL_10V mode is selected, the 1st output is set to the maximum value of the selected mode.
of the D/A converter is set to 10V)
DapiDASetVolt
This command sets a voltage to a channel of a D/A converter.
Description
This command sets a voltage to a channel of a D/A converter.
Definition
void DapiDASetVolt(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, float data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0 .. )
data=Indicates the voltage to be set [V]
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiDASetVolt(handle, 0, 5,4321);
// Sets the 1st output of the D/A converter to 5.4321 V
DapiDASetmA
This command sets a current to a channel of a D/A converter.
Description
This command sets a current to a channel of a D/A converter.
Definition
void DapiDASetmA(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, float data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0 .. )
data=Indicates the current that is written [mA]
Return value
None
Remark
This command is module-dependent. Of course, it only works if the module also supports current mode.
DapiSpecialCmdDA
This command sets the voltage values for a channel when switching on or after a timeout of a D/A converter.
Description
This command sets the voltage values for a channel when switching on or after a timeout of a D/A converter (EEPROM configuration).
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DA, cmd, ch, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the D/A converter (0, 1, 2, ..)
Resetting the settings to the default configuration
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_DEFAULT
Saving the configuration to the EEPROM
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_SAVE_EEPROM_CONFIG
Load the configuration from the EEPROM
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_EEPROM_CONFIG
Return value
None
Remark
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_DEFAULT
This command is used to load the default configuration of a D/A converter.
The D/A converter now has an output voltage of 0V.
DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_SAVE_EEPROM_CONFIG
This command saves the current D/A converter setting (voltage/current value, enable/disable and D/A converter mode) to the EEPROM.
DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_EEPROM_CONFIG
This command is used to set the D/A converter with the configuration stored in the EEPROM.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DA, DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_DEFAULT, 1, 0);
//Reset the EEPROM configuration to the default configuration for channel 1.
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DA, DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_SAVE_EEPROM_CONFIG, 3, 0);
//Saving the D/A converter settings in the EEPROM for channel 3.
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DA, DAPI_SPECIAL_DA_PAR_DA_LOAD_EEPROM_CONFIG, 2, 0);
//Set the D/A converter with the configuration stored in the EEPROM for channel 2.
Analog input functions
DapiADSetMode
This command configures the voltage range for an A/D converter.
Description
This command configures the voltage range for an A/D converter.
Definition
void DapiADSetMode(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG mode);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the A/D converter (0 .. )
mode=Indicates the mode for the channel
Return value
None
Remark
The following modes are supported:
(these depend on the A/D module used)
Unipolar voltages (does not apply to modules of the CAN-Box series)
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_10V
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_5V
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_2V5
Unipolar voltages of the CAN-Box series
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_40V
(nur CAN-Box 24V-Version)
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_60V
(nur CAN-Box 48V-Version)
Bipolar voltages
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_BIPOL_10V
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_BIPOL_5V
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_BIPOL_2V5
Currents
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_0_20mA
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_4_20mA
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_0_24mA
DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_0_50mA
Programming example
// Sets channel 0 to 0 ... 10V mode
DapiADSetMode(handle, 0, DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_10V);
DapiADGetMode
This command reads back the set mode of an A/D converter. For a mode description, see DapiADSetMode.
Description
This command reads back the set mode of an A/D converter. For a description of the mode, see DapiADSetMode.
Definition
ULONG DapiADGetMode(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the A/D converter (0 .. )
Return value
Mode of the A/D converter
Programming example
// Reads back the current mode of channel 1
unsigned long mode;
mode = DapiADGetMode(handle, 0);
// Check mode
if(mode == DAPI_ADDA_MODE_16BIT_UNIPOL_10V)
{
printf("Mode is 0 .. 10V");
}
DapiADGet
This command reads a data value from a channel of an A/D converter.
Description
This command reads a data value from a channel of an A/D converter.
Definition
ULONG DapiADGet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the A/D converter (0 .. )
Return value
Value from the A/D converter in digits
Remark
The value read back must be interpreted based on the set mode. If the mode is set to 0 ... 10V, a value of 0x8000 corresponds to 5V. However, if the mode is set to -10 ... 10V mode is set, the value 0x8000 corresponds to 0V.
Programming example
// Reads the value of channel 1
unsigned long data;
data = DapiADGet(handle, 0);
DapiADGetVolt
This command reads a data value from one channel of an A/D converter in volts.
Description
This command reads a data value from one channel of an A/D converter in volts.
Definition
float DapiADGetVolt(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the A/D converter (0 .. )
Return value
Value from the A/D converter in volts
Programming example
// Reads the value of channel 1 in volts
float data;
data = DapiADGetVolt(handle, 0);
DapiADGetmA
This command reads a data value of a channel of an A/D converter in mA.
Description
This command reads a data value of a channel of an A/D converter in mA.
Definition
float DapiADGetmA(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the channel of the A/D converter (0 .. )
Return value
Value from A/D converter in mA
Remark
This command is module-dependent. Of course, it only works if the module also supports current mode.
Programming example
// Reads the value of channel 1 in mA
float data;
data = DapiADGetmA(handle, 0);
DapiReadMultipleAD
This command saves the values of certain neighboring channels of an A/D converter simultaneously in an intermediate buffer. The values can then be read out one after the other.
Description
This command saves the values of certain neighboring channels of an A/D converter simultaneously in an intermediate buffer.
The values can then be read out one after the other. The advantage of this is that the A/D values are buffered simultaneously and the values can then be queried more quickly (compared to the DapiADGet command).
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_READ_MULTIPLE_AD, ULONG start_ch, ULONG end_ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
start_ch=Specifies the start channel of the A/D converter from which the values are buffered (0, 1, 2, ..).
end_ch=Specifies the end channel of the A/D converter up to which the values are buffered (0, 1, 2, ...).
Return value
None
Remark
The values buffered with the DapiReadMultipleAD command can then be read with the DapiADGetVolt, DapiADGetmA or DapiADGet commands. To ensure that the buffered value is actually read, the parameter "ch" must be logically linked with 0x8000 "or" for these functions (see examples).
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_READ_MULTIPLE_AD, 0, 15);
// Buffers the values of A/D channel 0..15
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_READ_MULTIPLE_AD, 0, 63);
// Buffers the values of A/D channel 0..63
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_READ_MULTIPLE_AD, 16, 31);
// Buffers the values of A/D channel 16..31
value = DapiADGetVolt(handle, 0x8000 | 0);
// Returns the buffered value of A/D channel 0 in volts.
value = DapiADGetmA(handle, 0x8000 | 15);
// Returns the buffered value of A/D channel 15 in mA.
value = DapiADGet(handle, 0x8000 | 63);
// Returns the buffered value of A/D channel 63 in digits.
DapiSpecialADFilterSet
This command can be used to set the A/D filter level of your A/D module.
Explanation
A/D converters with higher resolution are very precise measuring instruments that can detect even the smallest changes in the measurement signal. In practice
it often happens that electrical or electromagnetic disturbance variables affect the measurement signal via the connecting cable and distort it. The measurement signals can be smoothed and optimized with the help of an A/D filter. The software-based filter we use has already been integrated into the microcontroller that controls the A/D converter. Various filter levels can be set by software command and also
read back. The filter principle is based on averaging a sum of measurements. The higher the filter level is selected, the more measurements are used to calculate the average value. However, this also means that the sampling rate of the A/D converter is reduced as the filter level increases.
Description
This command can be used to set the A/D filter level of your A/D module. Depending on the module, the adjustable filter level may vary.
For a module with several submodules, the A/D filter level can be determined individually for each submodule.
If a 0 is transferred as the filter level, the filter level is deactivated.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_SET
par1=((filterlevel & 0xff) << 8) | (submodule_nr & 0xff)
filterlevel: specifies which filter level is to be set
submodule_nr: specifies the submodule on which the filter is to be set.
If the module has no submodules, the value 0xff is passed.
par2 = 0
Return value
None.
Remark
Each time the module is restarted, the A/D filter is initially switched off and can be
can be activated if required. It is therefore advisable to activate the A/D filter in the
initialization of your project.
Programming example
filterlevel = 10
submodule_nr = 0
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD,
DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_SET, ((filterlevel & 0xff) << 8)
| (submodule_nr & 0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of submodule 0 is set to 10
filterlevel = 5
submodule_nr = 3
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD,
DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_SET, ((filterlevel & 0xff) << 8)
| (submodule_nr & 0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of submodule 3 is set to 5
filterlevel = 6
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD,
DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_SET, ((filterlevel & 0xff) << 8)
| (0xff & 0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of the main module is set to 6 (only for modules without
submodule)
filterlevel = 2
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD,
DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_SET, ((filterlevel & 0xff) << 8)
| (0xff & 0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of the main module is set to 2 (only for modules without
submodule)
DapiSpecialADFilterGet
This command can be used to read out the A/D filter level of the A/D module.
Description
This command can be used to read out the A/D filter level of the A/D module.
For a module with submodules, the submodule number must be transferred.
Definition
void DT.Delib.DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_GET
par1=(submodule_nr & 0xff)
submodule_nr: specifies the submodule from which the filter is to be read.
If the module has no submodules, the value 0xff is transferred
par2 = 0
Return value
A/D filter level
Programming example
unsigned long filterlevel = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_GET, (0 &
0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of submodule 0 is read
unsigned long filterlevel = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_GET, (5 &
0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of submodule 5 is read
unsigned long filterlevel = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_AD, DAPI_SPECIAL_AD_FILTER_GET, (0xff
& 0xff) , 0);
// A/D filter of the main module is read(only for modules without
submodule)
Analog temperature functions
DapiTempGet
This command reads a temperature channel.
Description
This command reads a temperature channel.
Definition
float DapiTempGet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the input to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Temperature [°C]
Programming example
ret=DapiTempGet(handle, 0)
//returns the temperature of channel 0
DAPI_TEMP_GET_CHAN_GET_STATUS
This command reads out the status of the sensor.
Description
This command reads out the status of the sensor.
Definition
float DapiTempGet(ULONG handle, (ULONG par | ULONG ch));
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
par=DAPI_TEMP_GET_CHAN_GET_STATUS
ch=Specifies the number of the input to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Status of the sensor
Programming example
temp_status = DapiTempGet(handle, (DAPI_TEMP_GET_CHAN_GET_STATUS | ch));
if(temp_status == 0)
{
temp_status_text = "Status OK";
}
else
{
if((temp_status & 1) != 0)
{
temp_status_text = "Sensor offen";
}
if ((temp_status & 2) != 0) // Short GND
{
temp_status_text = "Short GND";
}
if ((temp_status & 4) != 0) // Short VCC
{
temp_status_text = "Short VCC";
}
}
CNT48 functions
DapiCnt48ModeSet
This command sets a counting mode (optionally also sub-mode) and input filter for a specific input counter channel.
Description
This command sets a counting mode (optionally also sub-mode) and input filter for a specific input counter channel.
Definition
void DapiCnt48ModeSet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG mode);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=number of the input counter channel whose mode is to be set (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
mode=Indicates the mode
Overview of available counter modes
Mode:
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE_X2
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE_X4
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_T
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_FREQUENCY
DAPI_CNT48_MODE_PWM
Submode:
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_NO_RESET
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_WITH_READ
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_NO_RESET
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_WITH_READ
Possible values for mode
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE |
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_NO_RESET
In this mode, the counter counts on a rising edge.
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE |
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_WITH_READ
In this mode, the counter counts on a rising edge. In addition, the counter is reset with every read operation.
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE |
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_ON_CH_7
In this mode, the counter counts on a rising edge. In addition, the counter can be reset via an external signal (last channel of the module = 1).
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE |
DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_LATCH_COMMON
With the command "DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_LATCH_GROUP8, 0, 0)", all 8 counter states of the input counters are written simultaneously to a latch. The latched counter reading can then be read out using this mode.
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_T
This mode is used to measure the period duration T. A 100 MHz counter serves as the basis for this.
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_FREQUENCY
In this mode, the number of rising edges within one second (=frequency) can be measured.
mode=DAPI_CNT48_MODE_PWM
This mode is used to measure the "high" and "low" time of a signal. This can then be used to determine the ratio (PWM).
In addition, all input counters can be combined with an input filter (with an or link). The following input filters are available for this purpose:
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_20ns
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_100ns
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_250ns
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_500ns
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_1us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_2_5us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_5us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_10us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_25us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_50us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_100us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_250us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_500us
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_1ms
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_2_5ms
DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_5ms
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Programming example
DapiCnt48ModeSet(handle, 0, DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE | DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_WITH_READ | DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_20ns);
// Input counter channel 0 counts all pulses <= 20ns on rising edge. The counter is also reset after a query.
DapiCnt48ModeSet(handle, 1, DAPI_CNT48_MODE_COUNT_RISING_EDGE | DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_RESET_ON_CH_7 | DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_500us);
// Input counter channel 1 counts all pulses <= 500us on rising edge. This counter can be reset with an external signal (ch7 = 1).
DapiCnt48ModeSet(handle, 2, DAPI_CNT48_MODE_PWM | DAPI_CNT48_FILTER_5ms);
// Input counter channel 2 measures all low/high times <= 5ms. The ratio is then determined (PWM).
DapiCnt48ModeGet
This command reads back the counting mode of a specific input counter channel.
Description
This command reads back the counting mode of a specific input counter channel.
Definition
ULONG DapiCnt48ModeGet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=number of the input counter channel whose mode is to be output (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Counting mode of the input counter channel.
(For more information / description of the bits -> see delib.h or manual "RO register assignment")
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Programming example
value = DapiCnt48ModeGet(handle, 0)
//Returns the counting mode of input counter channel 0
value = DapiCnt48ModeGet(handle, 3)
//Returns the counting mode of input counter channel 3
DapiCnt48CounterGet32
This command reads the first 32 bits of a 48-bit input counter.
Description
This command reads the first 32 bits of a 48-bit input counter.
Definition
ULONG DapiCnt48CounterGet32(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input counter channel to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Output of the counter value.
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 and RO-CNT/IGR modules.
Programming example
value = DapiCnt48CounterGet32(handle, 0);
//outputs the value of input counter channel 0
value = DapiCnt48CounterGet32(handle, 3);
//gibt den Wert des Eingangszählers Kanal 0 aus
DapiCnt48CounterGet48
This command reads a 48-bit counter of an input counter channel.
Description
This command reads a 48-bit counter of an input counter channel.
Definition
ULONGLONG DapiCnt48CounterGet48(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input counter channel to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Output of the counter value.
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 and RO-CNT/IGR modules.
Programming example
value = DapiCnt48CounterGet48(handle, 0);
//outputs the value of input counter channel 0
value = DapiCnt48CounterGet48(handle, 3);
//outputs the value of input counter channel 3
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCNT48ResetSingle
This command resets the counter reading of a single input counter.
Description
This command resets the counter reading of a single input counter.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_SINGLE, ULONG ch, 0)
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the input counter whose counter reading is to be reset (0, 1, 2, ..)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_SINGLE, 0, 0)
// Counter of input counter 0 is reset
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_SINGLE, 1, 0)
// Counter of input counter 1 is reset
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCNT48LatchGroup8
This command saves the counter readings of 8 input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch). In this way, all counter readings of the latch can be read out one after the other.
Description
This command saves the counter readings of 8 input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch).
In this way, all counter readings of the latch can be read out one after the other.
The special feature here is that it is possible to "freeze" the meter readings at the same time and the frozen readings (latch) can then be read out (slowly) one after the other.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_LATCH_GROUP8, ULONG ch, 0)
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the input counter from which the counter states of 8 input counters are latched (0, 8, 16, ...)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Please note that only the counter states of the input counters are latched for which the mode
"DAPI_CNT48_SUBMODE_LATCH_COMMON" mode was previously set. (-> DapiCnt48ModeSet)
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_LATCH_GROUP8, 0, 0)
// Counter of the input counters 0-7 are gelatched
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_LATCH_GROUP8, 8, 0)
// Meter of input meters 8-15 are latched
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCNT48ResetGroup8
This command simultaneously resets the counter readings of 8 input counters.
Description
This command resets the counter readings of 8 input counters simultaneously.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_GROUP8, ULONG ch, 0)
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the input counter from which the counter states of 8 input counters are reset (0, 8, 16, ...)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_GROUP8, 0, 0)
// Counter of input counters 0-7 are reset
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_RESET_GROUP8, 8, 0)
// Counter of input counters 8-15 are reset
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCNT48DIGet1
This command reads the input status (0/1) of a digital input counter channel.
Description
This command reads the input status (0/1) of a digital input counter channel.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_DI_GET1, ULONG ch, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input counter channel whose input status is to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
Status of the input counter (0/1)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-CNT8 module.
Programming example
value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_DI_GET1, 0, 0)
// Reads input status of input counter channel 1
value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_CNT48, DAPI_SPECIAL_CNT48_DI_GET1, 1, 0)
// Reads input status of input counter channel 2
Digital output functions
DapiDOSet1
This command sets a single output.
Description
This command sets a single output.
Definition
void DapiDOSet1(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be set (0 .. )
data=Indicates the data value to be written (0 / 1)
Return value
None
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DO
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DO, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch
Programming example
// Output 8 is set to 1
DapiDOSet1(handle, 7, 1);
DapiDOSet8
This command sets 8 digital outputs simultaneously.
Description
This command sets 8 digital outputs simultaneously.
Definition
void DapiDOSet8(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the output to be written from (0, 8, 16, 24, 32, ..)
data=Indicates the data values to be written
Return value
None
Programming example
// Outputs 9-12 are set to 0
// Outputs 13-16 are set to 1
DapiDOSet8(handle, 8, 0xf0);
DapiDOSet16
This command sets 16 digital outputs simultaneously.
Description
This command sets 16 digital outputs simultaneously.
Definition
void DapiDOSet16(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the output to be written from (0, 16, 32, ..)
data=Indicates the data values to be written
Return value
None
Programming example
// Outputs 1-8 are set to 0
// Outputs 9-16 are set to 1
DapiDOSet16(handle, 0, 0xff00);
DapiDOSet32
This command sets 32 digital outputs simultaneously.
Description
This command sets 32 digital outputs simultaneously.
Definition
void DapiDOSet32(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the output from which to write (0, 32, 64, ..)
data=Indicates the data values to be written
Return value
None
Programming example
// Write a value to the outputs
data = 0x0000ff00; // Outputs 9-16 are set to 1
DapiDOSet32(handle, 0, data); // Chan Start = 0
printf("Schreibe auf Ausgänge Daten=0x%x\n", data);
printf("Taste für weiter\n");
getch();
// ----------------------------------------------------
// Write a value to the outputs
data = 0x80000000; // Ausgang 32 wird auf 1 gesetzt
DapiDOSet32(handle, 0, data); // Chan Start = 0
printf("Schreibe auf Ausgänge Daten=0x%x\n", data);
printf("Taste für weiter\n");
getch();
// ----------------------------------------------------
// Write a value to the outputs
data = 0x80000000; // Ausgang 64 wird auf 1 gesetzt
DapiDOSet32(handle, 32, data); // Chan Start = 32
printf("Schreibe auf Ausgänge Daten=0x%x\n", data);
printf("Taste für weiter\n");
getch();
DapiDOSet64
This command simultaneously sets 64 digital outputs.
Description
This command sets 64 digital outputs simultaneously.
Definition
void DapiDOSet64(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONGLONG data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be written from (0, 64, ..)
data=Indicates the data values to be written
Return value
None
Programming example
// Outputs 1-32 are set to 0
// Outputs 33-64 are set to 1
DapiDOSet64(handle, 0, 0xffffffff00000000);
DapiDOReadback32
This command reads back the 32 digital outputs.
Description
This command reads back the 32 digital outputs.
Definition
ULONG DapiDOReadback32(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the output from which to read back (0, 32, 64, ..)
Return value
Status of 32 outputs.
Programming example
// Read back channel 1-32
unsigned long data;
data = DapiDOReadback32(handle, 0);
DapiDOReadback64
This command reads back the 64 digital outputs.
Description
This command reads back the 64 digital outputs.
Definition
ULONG DapiDOReadback64(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the output from which to read back (0, 32, 64, ..)
Return value
Status of 64 outputs.
Programming example
// Read back channel 1-64
unsigned long data;
data = DapiDOReadback64(handle, 0);
DapiDOSetBit32
This command can be used to switch outputs specifically to 1 without changing the states of the neighboring outputs.
Description
This command can be used to switch outputs specifically to 1 without changing the states of the neighboring outputs.
Definition
void DapiDOSetBit32(uint handle, uint ch, uint data);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
ch = Specifies the number of the output from which to write
data = Specifies the data value to be written (up to 32 bits)
Return value
None
Remark
Only the bits with a value of 1 in the data parameter are taken into account by the command.
Programming example
data = 0x1; // Output 0 would be changed to 1. The states of outputs 1-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xf; // Outputs 0-3 would be changed to 1. The states of outputs 4-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xff; // Outputs 0-7 would be changed to 1. The states of outputs 8-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xff000000; // Outputs 23-31 would be changed to 1. The states of outputs 0-21 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
DapiDOClrBit32
This command can be used to switch outputs specifically to 0 without changing the states of the neighboring outputs.
Description
This command can be used to switch outputs specifically to 0 without changing the states of the neighboring outputs.
Definition
void DapiDOClrBit32(uint handle, uint ch, uint data);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
ch = Specifies the number of the output from which to write
data = Specifies the data value to be written (up to 32 bits)
Return value
None
Remark
Only the bits with a value of 1 in the data parameter are taken into account by the command.
Programming example
data = 0x1; // Output 0 would be changed to 0. The states of outputs 1-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xf; // Outputs 0-3 would be changed to 0. The states of outputs 4-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xff; // Outputs 0-7 would be changed to 0. The states of outputs 8-31 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
data = 0xff000000; // Outputs 23-31 would be changed to 0. The states of outputs 0-21 won't be changed
DapiDOSetBit32(handle, 0, data);
DapiDOSet1_WithTimer
This function sets a digital output (ch) to a value (data - 0 or 1) for a specific time in ms.
Description
This function sets a digital output (ch) to a value (data - 0 or 1) for a specific time in ms.
Definition
void DapiDOSet1_WithTimer(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG data, ULONG time_ms);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be set (0 .. )
data=Indicates the data value to be written (0 / 1)
time_ms=Indicates the time in which the output is set [ms].
Return value
None
Remark
This command is supported by all output modules of the NET series, as well as by our RO-O8-R8 module.
This command loses its validity if it is overwritten with other values.
If you want to deactivate the command, it must be overwritten with time_ms=0.
Programming example
DapiDOSet1_WithTimer(handle, 2, 1, 1000);
//Setting channel 2 for 1000msec to 1
Digital input counter
DapiDIGet1
This command reads a single digital input.
Description
This command reads a single digital input.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGet1(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the input to be read (0, 1, 2, 3, .. )
Return value
State of the input (0/1)
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch
Programming example
// Read out 1 channel
unsigned long data;
data = DapiDIGet1(handle, 0);
DapiDIGet8
This command reads 8 digital inputs simultaneously.
Description
This command reads 8 digital inputs simultaneously.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGet8(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read (0, 8, 16, 24, .. )
Return value
State of the read inputs.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch (ch must be 0, 8, 16, ...)
Programming example
// Read out 8 channels
unsigned long data;
data = DapiDIGet8(handle, 0);
DapiDIGet16
This command reads 16 digital inputs simultaneously.
Description
This command reads 16 digital inputs simultaneously.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGet16(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read (0, 16, 32, ...)
Return value
State of the read inputs.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch (ch must be 0, 16, 32, ...)
Programming example
// Read out 16 channels
unsigned long data;
data = DapiDIGet16(handle, 0);
DapiDIGet32
This command reads 32 digital inputs simultaneously.
Description
This command reads 32 digital inputs simultaneously.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGet32(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read (0, 32, 64, ..)
Return value
State of the read inputs.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch (ch must be 0, 32, 64, ...)
Programming example
unsigned long data;
// ----------------------------------------------------
// Read a value from the inputs (Eingang 1-31)
data = (unsigned long) DapiDIGet32(handle, 0);
// Chan Start = 0
printf("Input 0-31 : 0x%x\n", data);
printf("Press any key to continue\n");
getch();
// ----------------------------------------------------
// Read a value from the inputs (input 32-64)
data = (unsigned long) DapiDIGet32(handle, 32);
// Chan Start = 32
printf("Input 32-64 : 0x%x\n", data);
printf("Press any key to continue\n");
getch();
DapiDIGet64
This command reads 64 digital inputs simultaneously.
Description
This command reads 64 digital inputs simultaneously.
Definition
ULONGLONG DapiDIGet64(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read (0, 64, ..)
Return value
State of the read inputs.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch (ch must be 0 or 64)
Programming example
// Read out 64 channels
ULONGLONG data;
data = DapiDIGet64(handle, 0);
DapiDIGetFF32
This command reads the flip-flops of the inputs and resets them.
Description
This command reads the flip-flops of the inputs and resets them.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGetFF32(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read (0, 32, 64, ..)
Return value
Status of 32 input status changes.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI_FF
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI_FF, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch (ch must be 0, 32, 64, ...)
DapiDIGetCounter
This command reads the input counter of a digital input.
Description
This command reads the input counter of a digital input.
Definition
ULONG DapiDIGetCounter(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG mode);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
ch=Specifies the number of the input from which to read.
mode=0 (normal counting function)
mode=DAPI_CNT_MODE_READ_WITH_RESET (read counter and reset counter directly)
mode=DAPI_CNT_MODE_READ_LATCHED (read out the stored counter reading)
Return value
Output of the counter value.
Requirements
The following SW feature bits must be supported by the module:
DAPI_SW_FEATURE_BIT_CFG_DI_CNT
The following conditions for the transfer parameters must be met:
maxCh = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_MODULE_CONFIG, DAPI_SPECIAL_GET_MODULE_CONFIG_PAR_DI_COUNTER, 0, 0);
maxCh > ch
Programming example
value = DapiDIGetCounter(handle, 0 ,0); // Counter of DI Chan 0 is read
value = DapiDIGetCounter(handle, 1 ,0); // Counter of DI Chan 1 is read
value = DapiDIGetCounter(handle, 8 ,0); // Counter of DI Chan 8 is read
value = DapiDIGetCounter(handle, 0 ,DAPI_CNT_MODE_READ_WITH_RESET); // Counter of DI Chan 0 is read AND reset
value = DapiDIGetCounter(handle, 1, DAPI_CNT_MODE_READ_LATCHED); // Reading the stored meter reading from DI Chan 1
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCounterLatchAll
This command saves the counter readings of all input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch).
Description
This command saves the counter readings of all input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch).
This allows all counter readings of the latch to be read out one after the other.
A special feature here is that it is possible to "freeze" the meter readings at the same time and the frozen readings (latch) can then be read out one after the other.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER, DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL, 0, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
mode=DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER (It is a counter command)
mode=DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL (Freezes all counter inputs and makes them available as a latch)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-O8-R8 time modules!
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER, DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL, 0, 0);
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialCounterLatchAllWithReset
This command saves the counter readings of all input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch). In addition, the counter readings of the input counters are subsequently reset.
Description
This command saves the counter readings of all input counters simultaneously in a buffer (latch). In addition, the counter readings of the input counters are subsequently reset.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER, DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL_WITH_RESET, 0, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module.
mode=DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER (It is a counter command)
mode=DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL_WITH_RESET (Freezes all counter inputs and makes them available as a latch and resets the counter of the input channels)
Remark
This command is only supported by our RO-O8-R8 time modules!
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_COUNTER, DAPI_SPECIAL_COUNTER_LATCH_ALL_WITH_RESET, 0, 0);
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialDIFilterValueSet
This command sets a filter [ms] in which time interval digital input channels are sampled.
Description
This command sets a filter [ms] in which time interval digital input channels are sampled.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FILTER_VALUE_SET, ULONG time_ms, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
time_ms=Time interval [ms] in which digital input channels are sampled.
Remark
This command only supports pulse times between 5ms and 255ms.
If no time is set, the default value is 100ms.
This command is not supported by our modules with Ethernet interface
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FILTER_VALUE_SET, 5, 0);
// Sets the time interval to 5ms
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FILTER_VALUE_SET, 150, 0);
// Sets the time interval to 150ms
DapiSpecialCommand - DapiSpecialDIFilterValueGet
This command returns the previously defined value of the time interval for sampling the digital input channels in [ms].
Description
This command returns the previously defined value of the time interval for sampling the digital input channels in [ms].
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FILTER_VALUE_GET, 0, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
Time [ms]
Remark
This command is not supported by our modules with Ethernet interface.
Programming example
value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FILTER_VALUE_GET, 0, 0);
//Returns the time interval for scanning the digital input channels.
DapiSpecialCommand - Dapi_Special_DI_FF_Filter_Value_Set
This command sets a filter [ms] in which time interval the input flip-flops and the input counters are queried.
Description
This command sets a filter [ms] in which time interval the input flip-flops and the input counters are queried.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FF_FILTER_VALUE_SET, ULONG time_ms, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
time_ms=Time interval [ms] in which digital input channels are sampled.
Remark
This command only supports pulse times between 5ms and 255ms.
If no time is set, the default value is 100ms.
This command is not supported by our modules with Ethernet interface.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FF_FILTER_VALUE_SET, 5, 0);
// Sets the time interval to 5ms
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI,
DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FF_FILTER_VALUE_SET, 150, 0);
// Sets the time interval to 150ms
DapiSpecialCommand - Dapi_Special_DI_FF_Filter_Value_Get
This command returns the previously defined value of the time interval for sampling the input flip-flops and the input counters in [ms].
Description
This command returns the previously defined value of the time interval for sampling the input flip-flops and the input counters in [ms].
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FF_FILTER_VALUE_GET, 0, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
Time [ms]
Remark
This command is not supported by our modules with Ethernet interface.
Programming example
value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_DI, DAPI_SPECIAL_DI_FF_FILTER_VALUE_GET, 0, 0);
//Returns the time interval for scanning the digital input channels.
Pulse gen functions
DapiPulseGenSet
This command generates a certain number of pulses with predefined low and high times.
Description
This command generates a certain number of pulses with predefined low and high times.
Definition
void DapiPulseGenSet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, ULONG mode, ULONG par0, ULONG par1, ULONG par2);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be set (0, 1, 2, .. )
mode=Mode with which pulses are generated (must always be 0).
par0=Number of pulses to be generated (par0=0 -> infinite number of pulses)
par1=Low time of the pulse ( t[ns] / 10 - 1)
par2=High time of the pulse ( t[ns] / 10 - 1)
Example for setting the low/high time (par1/par2)
500ns -> 500 / 10 - 1 = 49(dec)
7us -> 7,000 / 10 - 1 = 699(dec)
2.5ms -> 2,500,000 / 10 - 1 = 249,999(dec)
Return value
None
Remark
Only supported by our RO-CNT8 modules.
Programming example
DapiPulseGenSet(handle, 0, 0, 10, 29, 69);
// generates 10 pulses at pulse generator output 0 with a low time of 300ns and a high time of 700ns.
DapiPulseGenSet(handle, 3, 0, 100, 7999, 9999);
// generates 100 pulses at pulse generator output 3 with a low time of 80us and a high time of 100us.
DapiPulseGenSet(handle, 10, 0, 0, 249999, 299999);
// generates an infinite number of pulses at pulse generator output 10 with a low time of 2.5ms and a high time of 3ms.
PWM functions
DapiPWMOutSet
This command sets the PWM ratio of a PWM channel.
Description
This command sets the PWM ratio of a PWM channel
Definition
void DapiPWMOutSet(ULONG handle, ULONG ch, float data);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be set
data=PWM ratio from 0% to 100% in 1% steps
Minimum PWM ratio depends on the PWM frequency
10Hz data must be >= 0%
100Hz data must be >= 2%
250Hz data must be >= 3%
1000Hz data must be >= 9%
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiPWMOutSet(handle, 0, 50);
// Sets the pwm ratio of channel 1 to 50% (50% high, 50% low)
DapiPWMOutSet(handle, 1, 100);
// Sets the pwm ratio of channel 2 to 100% (100% high, 0% low)
DapiPWMOutReadback
This command reads the PWM ratio of a PWM channel.
Description
This command reads the PWM ratio of a PWM channel
Definition
float DapiPWMOutReadback(ULONG handle, ULONG ch);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
ch=Indicates the number of the output to be read
Return value
PWM ratio of the channel from 0% to 100%
Programming example
float data = DapiPWMOutReadback(handle, 0);
// Reads the pwm ratio of the first channel
float data = DapiPWMOutReadback(handle, 2);
// Reads the pwm ratio of the second channel
DapiSpecialCommand - DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_SET
This command sets the PWM frequency of the module.
Description
This command sets the PWM frequency of the module
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_PWM, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_SET
par1=channel area 0 (ch 0-15), 16 (ch 16-31) ... etc.
par2=Frequency = DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_10HZ, DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_100HZ, DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_250HZ or DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_1000Hz
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_PWM, DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_SET, 0, DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_100HZ);
// Sets the pwm frequency of the module to 100Hz
DapiSpecialCommand - DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_READBACK
This command reads the current PWM frequency of the module.
Description
This command reads the current PWM frequency of the module
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_PWM, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_READBACK
par1=0
par2=0
Return value
uint = DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_10HZ, DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_100HZ, DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_250HZ or DAPI_PWM_FREQUENCY_1000Hz
Programming example
uint frequency = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_PWM, DAPI_SPECIAL_PWM_FREQ_READBACK, 0, 0);
// Reads the pwm frequency of the module
Register functions
DapiWriteByte
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Definition
void DapiWriteByte(ULONG handle, ULONG adress, ULONG value);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
value=Specifies the data value that is written (8-bit)
Return value
None
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Data is written to register 0x10
DapiWriteByte(handle, 0x10, 0xFF);
DapiWriteWord
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Definition
void DapiWriteWord(ULONG handle, ULONG adress, ULONG value);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
value=Specifies the data value that is written (16-bit)
Return value
None
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Data is written to register 0x10
DapiWriteWord(handle, 0x10, 0xFFFF);
DapiWriteLong
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Definition
void DapiWriteLong(ULONG handle, ULONG adress, ULONG value);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
value=Specifies the data value that is written (32-bit)
Return value
None
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Data is written to register 0x10
DapiWriteLong(handle, 0x10, 0xFFFFFFFF);
DapiWriteLongLong
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register write command to the module.
Definition
void DapiWriteLongLong(ULONG handle, ULONG adress, ULONGLONG value);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
value=Specifies the data value that is written (64-bit)
Return value
None
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Data is written to register 0x10
DapiWriteLongLong(handle, 0x10, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF);
DapiReadByte
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Definition
ULONG DapiReadByte(ULONG handle, ULONG adress);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
Return value
Content of the register to be read (8-bit)
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programmierbeispiel
// Reads 8 bits from the address 0x0
ULONG data;
data = DapiReadByte(handle, 0x0);
DapiReadWord
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Definition
ULONG DapiReadWord(ULONG handle, ULONG adress);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
Return value
Content of the register to be read (16-bit)
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Reads 16 bits from the address 0x0
ULONG data;
data = DapiReadWord(handle, 0x0);
DapiReadLong
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Definition
ULONG DapiReadLong(ULONG handle, ULONG adress);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
adress=Address to be accessed
Return value
Content of the register to be read (32-bit)
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Reads 32 bits from the address 0x0
ULONG data;
data = DapiReadLong(handle, 0x0);
DapiReadLongLong
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Description
This command executes a direct register read command on the module.
Definition
ULONGLONG DapiReadLongLong(ULONG handle, ULONG address);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
address=Address to be accessed
Return value
Content of the register to be read (64-bit)
Remark
This should only be used by experienced programmers. This allows direct access to all available registers.
Programming example
// Reads 64 bits from the address 0x0
ULONGLONG data;
data = DapiReadLongLong(handle, 0x0);
Software FIFO functions
DapiSpecialCMDSWFifo
This command is used to set the software FIFO.
Description
This command is used to set the software FIFO.
A distinction is made between FIFO-OUT (fifo_instance 0 - 3) for D/A and DO applications
and FIFO-IN (fifo_instance 4 - 7) for A/D and DI applications.
Further information on the individual commands can be found in the following
chapters and our Fifo In/Out programming example.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, par2);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
cmd = Function to be executed
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO [0..7].
par2 = Value that is passed to the function
Remark
First, always define the submodule with the
DapiSpecialSWFifoSetSubmodule command!
DapiSpecialSWFifoInitAndClear
This command deletes existing data from the software FIFO memory and returns the FIFO mechanism to its initial state.
Description
This command deletes existing data from the software FIFO memory and
returns the FIFO mechanism to its initial state.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_INIT_AND_CLEAR
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Important
The interface and the submodules have separate software FIFOs,
therefore the DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_INIT_AND_CLEAR command must be applied to both.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_INIT_AND_CLEAR, fifo_instance, 0);
//Existing data is deleted from the FIFO memory.
DapiSpecialSWFifoSetIOModule
This command specifies the NET I/O module to which the software FIFO data is transferred.
Description
This command specifies the NET I/O module to which the data of the software FIFO
are transferred.
The submodule sequence that is connected to the interface module,
determines which submodule number you must specify.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_SET_IOMODULE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
par2 = Specifies the number of the I/O module (0, 1, 2, 3, ...)
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_SET_IOMODULE, fifo_instance, 2);
//The software FIFO transfers the data to NET-I/O module 2.
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetIOModule
This command returns the number of the NET I/O module to which the data is transferred.
Description
This command returns the number of the NET-I/O module to which the data is transferred.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_IOMODULE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_IOMODULE, fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Submodule = %lu\n", ret);
//The number of the NET I/O module is read out and displayed.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModActivate
This command activates the FIFO data transfer within the NET modules.
Description
This command activates the FIFO data transfer within the NET modules.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_ACTIVATE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_ACTIVATE, fifo_instance, 0);
//The automatic output of the FIFO data transmission is activated.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModDeactivate
This command deactivates the FIFO data transfer within the NET modules.
Description
This command deactivates the FIFO data transfer within the NET modules.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_DEACTIVATE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_DEACTIVATE, fifo_instance, 0);
//The automatic output of the FIFO data transmission is deactivated.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModSetChannel
This command specifies the channels to which the FIFO data is to be transferred by specifying the start and end channels.
Description
This command specifies the start and end channels into which the
the FIFO data is to be transferred.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, ch);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_CHANNEL
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
ch = Specifies the start and end channel
Programming example
unsigned long ch_start = 0; //Start with Channel 0
unsigned long ch_end = 1; //End with Channel 1
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_CHANNEL, fifo_instance,
((ch_end << 8) & 0xff00) | (ch_start & 0xff);
//The start and end channel is defined
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetChannel
This command shows the channels to which the data is transferred.
Description
This command shows the channels to which the data is transferred.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_CHANNEL
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of channels
Bit 0-7 Start channel
Bit 8-15 End channel
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_CHANNEL, fifo_instance,
0);
printf("Channel = %lu\n", ret);
//Shows the submodule channels into which the data
are transferred.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModSetFrequencyHz
This command specifies the frequency (in Hertz) at which the input is read and the output is written.
Description
This command specifies the frequency (in Hertz) with which ...
... is read on input.
... is written during output.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_FREQUENCY_HZ
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
par2 = Frequency in Hertz (Hz)
Remark
Permissible value range: min. 1Hz, max. depending on the module used
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_FREQUENCY_HZ,
fifo_instance, 10);
//Sets the frequency interval to 10Hz.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetFrequencyHz
This command shows the set frequency of the NET-I/O module in Hertz.
Description
This command shows the set frequency of the NET-I/O module in Hertz.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_FREQUENCY_HZ
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Frequency in Hertz (Hz)
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_FREQUENCY_HZ,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Frequency = %lu (Hz)\n", ret);
//Displays the previously set frequency of the NET I/O module.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModSetMode
This command sets the software FIFO mode.
Description
This command sets the software FIFO mode.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_MODE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
| par2 = Software FIFO Mode | Value(hex) |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_AD16 | 0x40 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_AD16_TS | 0xc0 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_AD18 | 0x41 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_AD18_TS | 0xc1 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_DI8 | 0x60 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_DI8_TS | 0xe0 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_DI16 | 0x61 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_MODE_IN_DI16_TS | 0xe1 |
Remark
The software FIFO mode can be set both with and without timestamp (TS).
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_SET_MODE, fifo_instance, 0);
//The software FIFO mode is set.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetMode
This command returns the previously set FIFO mode. This is currently not yet supported in the firmware.
Description
This command returns the previously set FIFO mode. Currently this
not yet supported in the firmware.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_MODE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
FIFO software mode
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_MODE, fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Mode = %lu\n", ret);
//Gives the previously set FIFO mode again.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModIOActivate
This command activates the FIFO I/O input/output.
Description
This command activates the FIFO I/O input/output.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_IO_ACTIVATE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_IO_ACTIVATE, fifo_instance,
0);
//The automatic output of the FIFO to the module is activated.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModIODeactivate
This command deactivates the FIFO I/O input/output.
Description
This command deactivates the FIFO I/O input/output.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_IO_DEACTIVATE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_IO_DEACTIVATE,
fifo_instance, 0);
//The automatic output of the FIFO to the module is deactivated.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetBytesPerSample
This command specifies how many bytes are required for writing to the D/A converter.
Description
This command specifies how many bytes are required for writing to the D/A converter.
Example: If 3 D/A channels are written to a 16-bit (2-byte) D/A converter, 3x2 bytes are required per sample. The value 6 is played back.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_BYTES_PER_SAMPLE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Bytes required per sample
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_BYTES_PER_SAMPLE, fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Required bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the required bytes per sample.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetBytesAvailable
This command specifies how many bytes are available for writing.
Description
This command specifies how many bytes are available for writing.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_BYTES_AVAILABLE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of bytes
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_BYTES_AVAILABLE,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Available bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Number of bytes.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetBytesFree
This command specifies how many bytes are still free in the software FIFO of the submodule.
Description
This command specifies how many bytes are still free in the software FIFO of the submodule.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_BYTES_FREE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of bytes
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_BYTES_FREE,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Free FIFO bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Number of bytes.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetStatTXCnt
Indicates how many packets were sent from the submodule to the Software Fifo.
Description
Indicates how many packets were sent from the submodule to the software Fifo.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_TX_CNT
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of bytes
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_TX_CNT,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Sent data packets = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the bytes
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetStatTXErrCnt
Indicates how often errors occurred when sending data packets to the Fifo software.
Description
Indicates how often errors occurred when sending data packets to the Fifo software.
Errors occur, for example, when the Fifo overflows.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_TX_ERR_CNT
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of errors that occurred when sending the bytes
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_TX_ERR_CNT,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Available bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the number of errors that occurred when sending the bytes
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetStatRXCnt
Indicates how many data packets were received by the Fifo software.
Description
Indicates how many data packets were received by the Fifo software.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_RX_CNT
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of bytes received
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_RX_CNT,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Available bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Number of bytes received.
DapiSpecialSWFifoIOModGetStatRXErrCnt
Indicates how often errors occurred when receiving the data packets.
Description
Indicates how often errors occurred when receiving the data packets.
Errors occur if there is no data in the FIFO, but a retrieval takes place.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_RX_ERR_CNT
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of errors that occurred when receiving the bytes
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_IOMOD_GET_STAT_RX_ERR_CNT,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Available bytes = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the number of errors that occurred when receiving the bytes
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetStatus
This command can be used to call up status values.
Description
This command can be used to call up status values.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_STATUS
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return-Wert
| Command | Description (FIFO status generates a return value...) |
Value(hex) |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_ STATUS_IS_ACTIVE |
... when the output of the D/A converter is active | 0x01 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_ STATUS_IO_IS_ACTIVE |
... if the output of the FIFO I/O is active | 0x02 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_ STATUS_FIFO_OVERFLOW |
... if too much data is written to the FIFO | 0x04 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_ STATUS_FIFO_UNDERRUN |
... if the FIFO is empty (an output is to take place at the I/O module, but there is no data in the FIFO) | 0x08 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_ STATUS_FIFO_OUT_OF_SYNC |
... if the FIFO communication within the modules is interrupted | 0x10 |
Programming example
unsigned long ret;
ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_STATU
S, fifo_instance, 0);
if((ret & 0x01) != 0) {printf("is_active");}
if((ret & 0x02) != 0) {printf("io_is_active");}
if((ret & 0x04) != 0) {printf("fifo_overflow");}
if((ret & 0x08) != 0) {printf("fifo_underrun");}
if((ret & 0x10) != 0) {printf("fifo_out_of_sync);}
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetStatusBytesOut
This command specifies how many bytes were sent.
Description
This command specifies how many bytes were sent.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_STATUS_BYTES_OUT
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Number of bytes sent
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_STATUS_BYTES_OUT,
fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Bytes gesendet = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the bytes already sent
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetBytesFree
This command is used to read out the free bytes in the software FIFO buffer.
Description
This command is used to read out the free bytes in the software FIFO buffer.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_BYTES_FREE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Free bytes of the software FIFO
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_BYTES_FREE, fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Freier Speicher = %lu\n", ret);
//Output of the bytes still free in the memory.
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetActivity
This command is used to call up the transmission status of the FIFO (whether active or inactive).
Description
This command is used to call up the transmission status of the FIFO (whether active or inactive).
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_ACTIVITY
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
Return = 0 (transmission is deactivated)
Return = 1 (transmission is activated)
Programming example
unsigned long ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_ACTIVITY, fifo_instance, 0);
printf("Status = %lu\n", ret);
//Transmission status is retrieved
DapiSpecialSWFifoGetInstanceType
This command can be used to read out which channel is an input or output channel.
Description
This command can be used to read out which channel is an input or output channel.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO, cmd, fifo_instance, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_INSTANCE_TYPE
fifo_instance = Specifies the instance of the software FIFO
Return value
| Command | Description | Value(hex) |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_INSTANCE_TYPE_FIFO_IN | ... Indicates whether the channel is an input | 0x01 |
| DAPI_SPECIAL_INSTANCE_TYPE_FIFO_OUT | ... Indicates whether the channel is an output | 0x02 |
Programming example
unsigned long ret;
for(int i=0;i!=10;++i)
{
ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle,
DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SW_FIFO,
DAPI_SPECIAL_SW_FIFO_GET_INSTANCE_TYPE, i, 0);
switch(ret)
{
case DAPI_SPECIAL_INSTANCE_TYPE_FIFO_IN:
printf("Instance %d = FIFO_IN\n\r", i);break;
case DAPI_SPECIAL_INSTANCE_TYPE_FIFO_OUT:
printf("Instance %d = FIFO_OUT\n\r", i);break;
default:
printf("Instance %d = INVALID\n\r", i);break;
}
}
//Indicates whether it is an input or output channel
DapiWriteFifo
This command writes data records to the software FIFO.
Description
This command writes data records to the software FIFO.
Definition
DapiWriteFifo(ULONG handle, ULONG fifo_instance, ULONG type, UCHAR * buffer, ULONG buffer_length);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
fifo_instance=Indicates the instance of the software FIFO
type=Indicates the FIFO type
buffer=Buffer for the data set to be sent
buffer_length=Length of the buffer
Programming example
DapiWriteFifo(handle, fifo_instance, type, buffer, buffer_length);
//Writes the data record to the software FIFO.
DapiReadFifo
This command reads out the software FIFO.
Description
This command reads out the software FIFO.
Definition
ULONG DapiReadFifo(ULONG handle, ULONG fifo_instance, ULONG type, UCHAR * buffer, ULONG buffer_length);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
fifo_instance=Indicates the instance of the software FIFO
type=Indicates the FIFO type
buffer=Buffer for the data set to be received
buffer_length=Length of the buffer
Return value
Length of the FIFO data set read out
Programming example
//Reads the data set from the software FIFO
DapiReadFifo(handle, fifo_instance, type, buffer, buffer_length);
Stepper motor functions
DapiStepperCommandEx
This extended command controls stepper motors.
Description
This extended command controls stepper motors.
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperCommandEx(ULONG handle, ULONG motor, ULONG cmd, ULONG par1, ULONG par2, ULONG par3, ULONG par4, ULONG par5, ULONG par6, ULONG par7);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
motor=Number of the motor to be addressed
cmd=Extended command
par1..7=Extended command-dependent parameters (see note)
Remark
See delib.h for the extended commands and the associated parameters.
DapiStepperCommand_GoPosition
This is used to move to a specific position. This command may only be executed if the motor is not disabled and no Go_Position or Go_Reference is executed.
Description
This is used to move to a specific position. This command may only be executed if the motor is not disabled and no Go_Position or Go_Reference is executed.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_POSITION, position, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
position=Position to be approached
Programming example
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_POSITION , go_pos_par, 0,0,0);
DapiStepperCommand_GoPosition_Relative
This is used to move to a relative position. In contrast to the GO_POSITION command, which moves to an absolute position, the current position is taken into account here.
Description
This is used to move to a relative position. In contrast to the GO_POSITION command, which moves to an absolute position, the current position is taken into account here. This command may only be executed if the motor is not "disabled" and no Go_Position or Go_Reference is executed.
Definition
void DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_POSITION_RELATIVE, go_pos_rel_par, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
go_pos_rel_par=Relative position to be approached
Programming example
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_POSITION_RELATIVE, 100, 0, 0, 0);
//Motor moves 100 steps to the right as seen from the current position.
DapiStepperCommand_GoRefswitch
The motor moves to the reference position.
Description
The motor moves to the reference position
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_REFSWITCH, par1, par2, par3, 0);
Parameter
Possible values for par1: (if several are required, the individual values must be added together)
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF1
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF2
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_LEFT
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_RIGHT
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_GO_POSITIVE
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_GO_NEGATIVE
DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_SET_POS_0
par2=Motor position offset (1/16 full step)
par3=Timeout time [ms]
Remark
Moving to the reference switch
First, the motor moves to reference position 1 or 2 (see par1).
You can specify whether reference switch 1 (DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF1) or reference switch 2 (DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF2) is to be approached.
The direction in which the motor starts can be selected. The parameter DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_GO_NEGATIVE is used to start to the left and the parameter DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_GO_POSITIVE is used to start to the right.
The speed GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH is used here (see DapiStepperCommand_SetMotorcharacteristic).
Moving out of the reference switch
The motor then moves out of the reference position at the speed GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH. You can choose whether the motor moves to the right or left side of the reference switch. The parameter DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_LEFT is used to move to the left edge and the parameter DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_RIGHT is used to move to the right edge.
Optional approach of an offset
After moving out of the reference switch, an offset can still be approached. If this parameter is not = 0 (par2), the motor moves to this offset at the speed GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET.
Zeroing the position of the motor
The parameter DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_SET_POS_0 can also be used to set whether the motor is now set to position 0.
Programming example
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GO_REFSWITCH, DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF1 + DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_LEFT + DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_REF_GO_POSITIVE + DAPI_STEPPER_GO_REFSWITCH_PAR_SET_POS_0, 0, 15000, 0);
DapiStepperCommand_SetPosition
This command is used to set the motor position. The resolution is 1/16 full step. This command may only be used when the motor is stopped.
Description
This command is used to set the motor position. The resolution is 1/16 full step. This command may only be used when the motor is stopped.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_POSITION, par1, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
par1=Motorposition
DapiStepperCommand_SetFrequency
This command is used to set the motor setpoint frequency. The motor frequency control is responsible for maintaining the acceleration/deceleration ramp.
Description
This command is used to set the target motor frequency. The motor frequency control maintains the acceleration/deceleration ramp. Step losses do not occur. The motor setpoint frequency is related to full step operation. The direction is selected via the sign.
The motor setpoint frequency must not exceed the maximum frequency, otherwise the command will be rejected.
If limit switch1 is closed, the motor can only be moved in the positive direction; if limit switch2 is closed, the motor can only be moved in the negative direction, otherwise the command is rejected.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_FREQUENCY, par1, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
par1=set motor frequency [Hz]
DapiStepperCommand_GetFrequency
This command is used to query the motor frequency. This command may always be used.
Description
This command is used to query the motor frequency. This command may always be used.
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_FREQUENCY, 0, 0 ,0 ,0);
Return value
Motor frequency [Hz]
DapiStepperCommand_SetFrequencyDirectly
This command is used to set the motor frequency. The motor frequency control has no function. The user is responsible for maintaining the acceleration/deceleration ramp.
Description
This command is used to set the motor frequency. The motor frequency control has no function. The user is responsible for maintaining the acceleration/deceleration ramp. Step losses may occur if the ramp is not adhered to.
The motor frequency is based on full step operation. The direction is selected via the sign.
The frequency must not exceed the maximum frequency.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_FREQUENCY_DIRECTLY, par1, 0 ,0 ,0);
Parameter
par1=Motor frequency [Hz]
DapiStepperCMDStop
This command is used to stop the motor, the braking ramp is maintained.
Description
This command is used to stop the motor while maintaining the braking ramp.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_STOP, 0, 0, 0, 0);
DapiStepperCommand_Fullstop
This command is used to stop the motor immediately; the braking ramp is not maintained. The motor position may no longer be correct afterwards, as the motor is stopped in an uncontrolled manner.
Description
This command is used to stop the motor immediately; the braking ramp is not maintained. The motor position may no longer be correct afterwards, as the motor is stopped in an uncontrolled manner.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_FULLSTOP, 0, 0, 0, 0);
Programming example
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_FULLSTOP , 0, 0, 0, 0);
DapiStepperCommand_Disable
This command is used to disable/enable the motor, the motor then no longer moves/or moves again. This command may only be used when the motor is at a standstill.
Description
This command is used to disable/enable the motor, the motor then no longer moves/or moves again. This command may only be used when the motor is at a standstill.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_DISABLE, par1, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
par1=Disablemode (0=Normal function / 1=Disable)
DapiStepperCommand_SetMotorcharacteristic
This is used to set new motor configurations.
Description
This is used to set new motor configurations.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC, par1, par2, 0, 0);
Parameter
Set parameter step mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STEPMODE
par2=0 (full step mode)
par2=1 (half-step mode)
par2=2 (quarter-step mode)
par2=3 (eighth step mode)
par2=4 (sixteenth step mode)
Set parameter GO frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOFREQUENCY
par2=Speed [full step / s] - related to full step frequency - (maximum value=5000)
Set parameter start frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STARTFREQUENCY
par2=Start frequency [full step / s] - related to full step frequency - (maximum value=5000)
Set parameter stop frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STOPFREQUENCY
par2=Stop frequency [full step / s] - related to full step frequency - (maximum value=5000)
Set parameter max frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_MAXFREQUENCY
par2=Maximum frequency [full step / s] - related to full step frequency - (maximum value=5000)
Set parameter acceleration level
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ACCELERATIONSLOPE
par2=Acceleration ramp [full step / 10ms] - (maximum value=1000)
Set parameter deceleration loop
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_DECELERATIONSLOPE
par2= Braking ramp [full step / 10ms] - (maximum value=1000)
Set parameter phasecurrent
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_PHASECURRENT
par2=Phase current [mA] - (maximum value = 1500)
Set parameter hold phasecurrent
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDPHASECURRENT
par2=Phase current at motor standstill [mA] - (maximum value=1500)
Set parameter hold time
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDTIME
par2=Time in which the holding current flows after motor stop [ms]
par2=-1 / FFFF hex / 65535 dec (infinite time)
Set parameter status LED mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STATUSLEDMODE
par2=Operating mode of the status LED
par2=0 = (MOVE - LED lights up during motor movement)
par2=1 = (STOP - LED lights up when motor is at a standstill)
par2=2 = (ENDSW1 - LED lights up when limit switch1 is closed)
par2=3 = (ENDSW2 - LED lights up when limit switch2 is closed)
par2=4 = (REFSW1 - LED lights up when reference switch1 is closed)
par2=5 = (REFSW2 - LED lights up when reference switch2 is closed)
Set parameter Invert-END-Switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW1
par2=Invert function of limit switch1 (0=normal / 1=invert)
Set parameter invert-END-Switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW2
par2=Invert function of limit switch2 (0=normal / 1=invert)
Set parameter invert-ref-switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW1
par2=Invert function of reference switch1 (0=normal / 1=invert)
Set parameter invert-ref-switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW2
par2=Invert function of reference switch switch2 (0=normal / 1=invert)
Set parameter invert direction
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_DIRECTION
par2=Invert all directions (0=normal / 1=invert)
Set parameter end switch stop mode
par1= DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ENDSWITCH_STOPMODE
par2=Setting the stop behavior (0=Fullstop / 1=Stop)
Set parameter GoReferenceFrequency (ATTENTION: This parameter is no longer supported!)
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY
Note: This parameter is completely replaced by the following three parameters.
Set parameter GoReferenceFrequnecyToEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH
par2=Speed at which the end switch is approached (frequency [full step / s] - (maximum value=5000))
Set parameter GoReferenceFrequencyAfterEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH
par2=Speed at which the limit switch is run (frequency [full step / s] - (maximum value=5000))
Set parameter GoReferenceFrequencyToOffset
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET
par2=Speed at which the optional offset is approached (frequency [full step / s] - (maximum value=5000))
Programming example
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STEPMODE, 4,0,0); // Step mode (full, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth step)
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOFREQUENCY, 1000,0,0); // Step mode at motor stop (full, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth step)
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STARTFREQUENCY, 100,0,0); // Start frequency [full step / s]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STOPFREQUENCY, 100,0,0); // Stop frequency [full step / s]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_MAXFREQUENCY, 3500,0,0); // Maximum frequency [full step / s]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ACCELERATIONSLOPE, 20,0,0); // Acceleration in [full steps / ms]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_DECELERATIONSLOPE, 20,0,0); // Braking in [full steps / ms]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_PHASECURRENT, 750,0,0); // Phase current [mA]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDPHASECURRENT, 500,0,0); // Phase current at motor standstill [mA]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDTIME, 15000,0,0); // Time in which the holding current flows after motor stop [s]
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STATUSLEDMODE, 0,0,0); // Operating mode of the status LED
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW1, 0,0,0); // Invert function of limit switch1
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW2, 0,0,0); // inverted function of the limit switch2
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW1, 0,0,0); // inverted function of the reference switch switch1
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW2, 0,0,0); // inverted function of the reference switch switch2
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_DIRECTION, 0,0,0); // invert all directions
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ENDSWITCH_STOPMODE, 0,0,0); // Setting the stop behavior
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH, 100,0,0); //Setting the speed at which the limit switch is approached.
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH , 200,0,0); //Setting the speed at which the limit switch is moved.
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET, 300,0,0); //Setting the speed at which the optional offset is approached.
DapiStepperCommand_GetMotorcharacteristic
This is used to read out the motor-specific parameter. This command may always be used. It is divided into sub-commands that are analogous to the parameters of DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC.
Description
This is used to read out the motor-specific parameter. This command may always be used. It is divided into sub-commands that are analogous to the parameters of DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_SET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC.
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC, par1, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
Query parameter step mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STEPMODE
Query parameter GO frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOFREQUENCY
Query parameter start frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STARTFREQUENCY
Query parameter stop frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STOPFREQUENCY
Query parameter max frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_MAXFREQUENCY
Query parameter acceleration level
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ACCELERATIONSLOPE
Query parameter deceleration loop
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_DECELERATIONSLOPE
Query parameter phasecurrent
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_PHASECURRENT
Query parameter hold phasecurrent
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDPHASECURRENT
Query parameter hold time
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDTIME
Query parameter status LED mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STATUSLEDMODE
Query parameter invert-END switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW1
Query parameter invert-END-Switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW2
Query parameter invert-ref-switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW1
Query parameter invert-ref-switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW2
Query parameter invert direction
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_DIRECTION
Query parameter end switch stop mode
par1= DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ENDSWITCH_STOPMODE
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequency (ATTENTION: This parameter is no longer supported!)
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY
Note: This parameter is completely replaced by the following three parameters.
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequnecyToEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequencyAfterEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequencyToOffSet
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET
Return value
Query parameter step mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STEPMODE
return=0 (full step mode)
return=1 (half-step mode)
return=2 (quarter step mode)
return=3 (eighth step mode)
return=4 (sixteenth step mode)
Query parameter GO frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOFREQUENCY
return=Speed [full step / s] - related to full step
Query parameter start frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STARTFREQUENCY
return=Start frequency [full step / s]
Query parameter stop frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STOPFREQUENCY
return=Stop frequency [full step / s]
Query parameter max frequency
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_MAXFREQUENCY
return=maximum frequency [full step / s]
Query parameter acceleration loop
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ACCELERATIONSLOPE
return=Acceleration ramp [full step / 10ms]
Query parameter deceleration loop
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_DECELERATIONSLOPE
return=Braking ramp [full step / 10ms]
Query parameter phase curves
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_PHASECURRENT
return=Phase current [mA]
Query parameter hold phasecurrent
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDPHASECURRENT
return= Phase current at motor standstill [mA]
Query parameter hold time
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDTIME
return=Time in which the holding current flows after motor stop [ms]
Query parameter status LED mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STATUSLEDMODE
return=Operating mode of the status LED
return=0 (MOVE - LED lights up during motor movement)
return=1 (HALT - LED lights up when motor is at a standstill)
return=2 (ENDSW1 - LED lights up when limit switch1 is closed)
return=3 (ENDSW2 - LED lights up when limit switch2 is closed)
return=4 (REFSW1 - LED lights up when reference switch1 is closed)
return=5 (REFSW2 - LED lights up when reference switch2 is closed)
Query parameter Invert-END-Switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW1
return=Limit switch1 is inverted (0=normal / 1=invert)
Query parameter invert-END-Switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW2
return=End switch2 is inverted (0=normal / 1=invert)
Query parameter invert-ref-switch1
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW1
return=Reference switch switch1 is inverted (0=normal / 1=invert)
Query parameter invert-ref-switch2
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW2
return=Reference switch switch2 is inverted (0=normal / 1=invert)
Query parameter invert direction
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_DIRECTION
return=Direction information is inverted (0=normal / 1=invert)
Query parameter end switch stop mode
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ENDSWITCH_STOPMODE
return=Setting the stop behavior (0=Fullstop / 1=Stop)
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequnecyToEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH
return=Frequency [full step / s]
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequencyAfterEndSwitch
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH
return=Frequency [full step / s]
Query parameter GoReferenceFrequencyToOffset
par1=DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET
return=Frequency [full step / s]
Programming example
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STEPMODE, 0, 0, 0); // Step mode (full, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth step)
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOFREQUENCY, 0,0,0); // Step mode at motor stop (full, half, quarter, eighth, sixteenth step)
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STARTFREQUENCY, 0,0,0); // Start frequency [full step / s]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STOPFREQUENCY, 0,0,0); // Stop frequency [full step / s]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_MAXFREQUENCY, 0,0,0); // Maximum frequency [full step / s]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ACCELERATIONSLOPE, 0,0,0); // Acceleration in [full steps / ms]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_DECELERATIONSLOPE, 0,0,0); // Braking in [full steps / ms]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_PHASECURRENT, 0,0,0); // Phase current [mA]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDPHASECURRENT, 0,0,0); // Phase current at motor standstill [mA]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_HOLDTIME, 0,0,0); // Time in which the holding current flows after motor stop [s]
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_STATUSLEDMODE, 0,0,0); // Operating mode of the status LED
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW1, 0,0,0); // Invert function of limit switch1
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_ENDSW2, 0,0,0); // Inverted function of the limit switch2
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW1, 0,0,0); // inverted function of the reference switch switch1
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_REFSW2, 0,0,0); // inverted function of the reference switch switch2
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_INVERT_DIRECTION, 0,0,0); // invert all directions
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC , DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_ENDSWITCH_STOPMODE, 0,0,0); // Setting the stop behavior
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC ,
DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOENDSWITCH, 0,0,0); // Query the speed at which the limit switch is approached.
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC ,
DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_AFTERENDSWITCH, 0,0,0); // Query the speed at which the limit switch is moved.
value = DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC ,
DAPI_STEPPER_MOTORCHAR_PAR_GOREFERENCEFREQUENCY_TOOFFSET, 0,0,0); // Query the speed at which the optional offset is approached
DapiStepperCommand_Motorcharacteristic_EEPROMSave
The current motor characteristics of the motor are saved in the EEPROM.
Description
The current motor characteristics of the motor are saved in the EEPROM.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC_EEPROM_SAVE, 0, 0, 0, 0);
DapiStepperCommand_Motorcharacteristic_EEPROMSLoad
The motor characteristics of the motor are loaded from the EEPROM.
Description
The motor characteristics of the motor are loaded from the EEPROM.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC_EEPROM_LOAD, 0, 0, 0, 0);
DapiStepperCommand_MotorcharacteristicLoadDefault
The motor characteristics of the motor are reset to default values.
Description
The motor characteristics of the motor are reset to default values.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_MOTORCHARACTERISTIC_LOAD_DEFAULT, 0, 0, 0, 0);
Remark
The default values are as follows:
- Step mode: Full step
- Step frequency at go position [full step / s]: 1000 Hz
- Start frequency [full step / s]: 200Hz
- Stop frequency [full step / s]: 200Hz
- Maximum step frequency [full step / s]: 3000Hz
- Acceleration ramp [Hz/10ms]: 10Hz/10ms
- Braking ramp [Hz/10ms]: 10Hz/10ms
- Phase current 0..1.5A [1mA]: 750mA
- Holding current 0..1.5A [1mA]: 500mA
- Hold time 0..infinite [ms]: 15000ms
- Status_LED function: Move
- Function of limit switch1: not inverted
- Function of limit switch2: not inverted
- Function of reference switch1: not inverted
- Function of reference switch2: not inverted
- Function of all direction information: not inverted
- Limit switch mode: Full stop
- Step frequency for Go reference [full step / s]: 1000 Hz
DapiStepperCommand_GetCPUTemp
The temperature of the CPU is queried.
Description
The temperature of the CPU is queried.
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_CPU_TEMP, 0, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd=DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_CPU_TEMP
Return value
Temperature [°C]
DapiStepperCommand_GetMotorSupplyVoltage
This is used to query the supply voltage of the motor.
Description
This is used to query the supply voltage of the motor.
Definition
DapiStepperCommand(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTOR_SUPPLY_VOLTAGE, 0, 0, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd=DAPI_STEPPER_CMD_GET_MOTOR_SUPPLY_VOLTAGE
Return value
Motor supply voltage in [mV]
DapiStepperCommand_GetActivity
This is used to query various status information (e.g. motor current activity, etc.).
Description
This is used to query various status information (e.g. motor current activity, etc.).
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_ACTIVITY);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
motor=Number of the motor to be addressed
Return value
Bit Command Description
0 DISABLE Motor must not move
1 MOTOR CURRENT ACTIVE Motor current is active
2 HOLD CURRENT ACTIVE Holding current is active
3 GOPOSITIONACTIV GoPosition is active
4 GOPOSITION BRAKING GoPosition braking is active
5 GOREFERENCEACTIV GoReference is active
Programming example
ret = DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_ACTIVITY);
DapiStepperCommand_GetPosition
This is used to read a specific position.
Description
This is used to read a specific position
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, cmd);
Parameter
cmd=DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_POSITION
Return value
The current motor position is returned in 1/16 step units
Programming example
value = DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_POSITION);
DapiStepperCommand_GetSwitch
This is used to query the status of the switches.
Description
This is used to query the status of the switches
Definition
ULONG DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, cmd);
Parameter
cmd=DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_SWITCH
Return value
The status of the switches is returned:
Bit0: ENDSWITCH1; 1 = Limit switch1 is closed
Bit1: LIMIT SWITCH2; 1 = Limit switch2 is closed
Bit2: REFERENCE SWITCH1; 1 = Reference switch1 is closed
Bit3: REF SWITCH2; 1 = Reference switch2 is closed
Programming example
pos = DapiStepperGetStatus(handle, motor, DAPI_STEPPER_STATUS_GET_SWITCH);
Timeout protection function
DapiSpecialCMDTimeout
This command is used to set the timeout protection function.
Description
This command is used to set the timeout protection function.
There are three different timeout methods since 2021.
"normal" timeout
This is the timeout that our modules have had since 2009.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is longer than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "2".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible, but the timeout is no longer active. Only when it has been reactivated.
"auto reactivate" timeout
This is a timeout mode implemented since 2021, which automatically reactivates the timeout after the timeout event occurs.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is longer than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "4".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible. AND the timeout is still active. If the timeout time is exceeded again, the outputs are switched off again.
"secure outputs" timeout
This is a timeout mode implemented since 2021, which prevents write access to the outputs after the timeout event occurs, thus ensuring that the software must first restore a "secure" state of the outputs, as the module's timeout mechanism has changed the outputs to predefined values.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is longer than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "6".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is NOT possible. The outputs can only be written to after the timeout has been reactivated or deactivated.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
cmd = function to be executed
par1 = Value that is passed to the function
par2 = Value that is passed to the function
DapiSpecialTimeoutSetValueSec
This command is used to set the timeout time.
Description
This command is used to set the timeout time.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_SET_VALUE_SEC
par1 = seconds [s]
par2 = milliseconds [100ms] (value 6 = 600ms)
Remark
The permissible value range of the time specification is between 0.1 seconds and 6553 seconds
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_SET_VALUE_SEC, 3, 7);
// The time of the timeout is set to 3.7 sec.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivate
This command activates the "normal" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "normal" timeout.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ...the timeout status is set to "2"
- ...the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible, but the timeout is no longer active.
Only when it has been reactivated.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE, 0, 0);
// The "normal" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivateAutoReactivate
This command activates the "auto reactivate" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "auto reactivate" timeout.
In this mode, the timeout is automatically reactivated after the timeout event.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ..the timeout status is set to "4"
- ...the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible AND the timeout is still active.
If the timeout time is exceeded again, the outputs are switched off again.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_AUTO_REACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_AUTO_REACTIVATE, 0, 0);
// The "auto reactivate" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivateSecureOutputs
This command activates the "secure outputs" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "secure outputs" timeout.
In this mode, write access to the outputs is prevented after a timeout event.
This ensures that the software must first restore a "secure" state of the outputs,
as the module's timeout mechanism has changed the outputs to predefined values.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ..the timeout status is set to "6"
- ..the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is NOT possible. Only after reactivating the
timeout or deactivating the timeout, the outputs can be written to.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_SECURE_OUTPUTS
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_SECURE_OUTPUTS, 0, 0);
// The "secure outputs" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDeactivate
This command deactivates the timeout.
Description
This command deactivates the timeout.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DEACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DEACTIVATE, 0, 0);
// The timeout is deactivated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutGetStatus
This command is used to read out the timeout status.
Description
This command is used to read out the timeout status.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS
Return value
Return = 0 (timeout is deactivated)
Values for the "normal" timeout
Return = 1 (timeout "normal" is activated)
Return = 2 (timeout "normal" has taken place)
Values for the "auto reactivate" timeout
Return = 3 ("auto reactivate" timeout is activated)
Return = 4 ("auto reactivate" timeout has occurred once or several times)
Values for the "secure" timeout
Return = 5 ("secure" timeout is activated)
Return = 6 (Timeout "secure" has taken place. Writing to the outputs is prevented in this status)
Programming example
unsigned long status = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS, 0, 0);
printf("Status = %ul\n", status);
//Query the timeout status with output.
Timeout protection function
DapiSpecialCMDTimeout
This command is used to set the timeout protection function.
Description
This command is used to set the timeout protection function.
There are three different timeout methods since 2021.
"normal" timeout
This is the timeout that our modules have had since 2009.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is longer than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "2".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible, but the timeout is no longer active. Only when it has been reactivated.
"auto reactivate" timeout
This is a timeout mode implemented since 2021, which automatically reactivates the timeout after the timeout event occurs.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is greater than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "4".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible. AND the timeout is still active. If the timeout time is exceeded again, the outputs are switched off again.
"secure outputs" timeout
This is a timeout mode implemented since 2021, which prevents write access to the outputs after the timeout event occurs, thus ensuring that the software must first restore a "secure" state of the outputs, as the module's timeout mechanism has changed the outputs to predefined values.
Procedure for the timeout command:
The timeout is activated by command.
If a so-called timeout event then occurs (pause between two accesses to the module is longer than the permitted timeout time), the following happens:
- All outputs are switched off.
- The timeout status changes to "6".
- The timeout LED goes on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is NOT possible. The outputs can only be written to after the timeout has been reactivated or deactivated.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
cmd = function to be executed
par1 = value that is passed to the function
par2 = Value that is passed to the function
DapiSpecialTimeoutSetValueSec
This command is used to set the timeout time.
Description
This command is used to set the timeout time.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, par1, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_SET_VALUE_SEC
par1 = seconds [s]
par2 = milliseconds [100ms] (value 6 = 600ms)
Remark
The permissible value range of the time specification is between 0.1 seconds and 6553 seconds
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_SET_VALUE_SEC, 3, 7);
//The timeout time is set to 3.7 sec.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivate
This command activates the "normal" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "normal" timeout.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ...the timeout status is set to "2"
- ...the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible, but the timeout is no longer active.
Only when it has been reactivated.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE, 0, 0);
//The "normal" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivateAutoReactivate
This command activates the "auto reactivate" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "auto reactivate" timeout.
In this mode, the timeout is automatically reactivated after the timeout event.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ..the timeout status is set to "4"
- ...the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is then still possible AND the timeout is still active.
If the timeout time is exceeded again, the outputs are switched off again.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_AUTO_REACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_AUTO_REACTIVATE, 0, 0);
//The "auto reactivate" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutActivateSecureOutputs
This command activates the "secure outputs" timeout.
Description
This command activates the "secure outputs" timeout.
In this mode, write access to the outputs is prevented after a timeout event.
This ensures that the software must first restore a "secure" state of the outputs,
as the module's timeout mechanism has changed the outputs to predefined values.
After the timeout event...
- ...all outputs are switched off
- ..the timeout status is set to "6"
- ..the timeout LED is switched on (for modules that have such a status)
Further access to the outputs is NOT possible. Only after reactivating the
timeout or deactivating the timeout, the outputs can be written to.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_SECURE_OUTPUTS
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_ACTIVATE_SECURE_OUTPUTS, 0, 0);
//The "secure outputs" timeout is activated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDeactivate
This command deactivates the timeout.
Description
This command deactivates the timeout.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DEACTIVATE
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DEACTIVATE, 0, 0);
//The timeout is deactivated.
DapiSpecialTimeoutGetStatus
This command is used to read out the timeout status.
Description
This command is used to read out the timeout status.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS
Return value
Return = 0 (timeout is deactivated)
Values for the "normal" timeout
Return = 1 (timeout "normal" is activated)
Return = 2 (timeout "normal" has taken place)
Values for the "auto reactivate" timeout
Return = 3 ("auto reactivate" timeout is activated)
Return = 4 ("auto reactivate" timeout has occurred once or several times)
Values for the "secure" timeout
Return = 5 ("secure" timeout is activated)
Return = 6 (Timeout "secure" has taken place. Writing to the outputs is prevented in this status)
Programming example
unsigned long status = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_GET_STATUS, 0, 0);
printf("Status = %ul\n", status);
// Query the timeout status with output.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDoValueMaskWRSet32
This command activates relays in the event of a timeout.
Description
This command determines the outputs that are to be set in the event of a timeout.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, ch, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_WR_SET32
ch = Specifies the number of the output from which to write (0, 32, 64, ..)
par2 = [32 Bit] Specifies the outputs which are to be activated in the event of a timeout
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_WR_SET32, 0, 0xff);
//The first 8 relays are switched on in the event of a timeout.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDoValueMaskRDSet32
This command is used to read out the transferred values.
Description
This command is used to read the transferred values
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_RD_SET32
Return value
[32 bit] Value that is transferred to the SET command
Programming example
unsigned long value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_RD_SET32, 0, 0);
printf("%0x\n", value);
//The value that was transferred to the SET command is read out and displayed.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDoValueMaskWRClr32
This command deactivates relays in the event of a timeout.
Description
This command determines the outputs that are to be switched off in the event of a timeout.
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, ch, par2);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_WR_CLR32
ch = Specifies the number of the output from which to write (0, 32, 64, ..)
par2 = [32 Bit] Specifies the outputs that are to be deactivated in the event of a timeout
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_WR_CLR32, 0, 0xff);
// The first 8 relays are switched off in the event of a timeout.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDoValueMaskRDClr32
This command is used to read out the transferred values.
Description
This command is used to read out the transferred values.
Definition
LONG DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_RD_CLR32
Return value
[32 bit] Value that is transferred to the CLR command
Programming example
unsigned long value = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_MASK_RD_CLR32, 0, 0);
printf("%0x\n", value);
//The value that was transferred to the CLR command is read out and displayed.
DapiSpecialTimeoutDoValueLoadDefault
Resets the SET and CLR values to the original value.
Description
Resets the SET and CLR values to the default value.
(SET value = 0, CLR value = FFFFFFFFFF)
Definition
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT, cmd, 0, 0);
Parameter
cmd = DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_LOAD_DEFAULT
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_TIMEOUT,
DAPI_SPECIAL_TIMEOUT_DO_VALUE_LOAD_DEFAULT, 0, 0);
//SET and CRL values are set to the default value.
TTL functions
DapiSpecialCMDSetDirDX_1
This command sets the direction of 8 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (1-bit wise).
Description
This command sets the direction of 8 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (1-bit wise).
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, ULONG ch, ULONG dir, 0);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
ch = Must always be 0!
dir = Indicates the direction for 8 channels (1=output / 0=input) / bit 0 stands for channel 0, bit 1 for channel 1 ...
Return value
None
Remark
Not compatible with USB-TTL-32/64.
Use the DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8 command for these modules.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x01 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x02 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH1 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x04 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH2 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x08 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH3 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x10 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH4 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x20 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH5 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x40 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH6 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x80 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH7 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0x0f , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-3 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1, 0, 0xff , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-7 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCMDSetDirDX_8
This command sets the direction of up to 64 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (8-bit wise). 1-bit represents 8 TTL inputs/outputs.
Description
This command sets the direction of up to 64 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (8-bit wise).
1-bit represents 8 TTL inputs/outputs.
Definition
void DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, ULONG ch, ULONG dir, 0);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
ch = Must always be 0!
dir = (8-bit) specifies the direction for up to 64 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs. (1=output / 0=input)
Return value
None
Remark
Only compatible with USB-TTL-32/64.
For other TTL products, use the DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_1 command.
Programming example
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0x1 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-7 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0x3 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-15 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0xc , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH16-31 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0x33 , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-15 and CH32-47 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_SET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0xff , 0);
// Set Dir of TTL-I/O CH0-63 to output, others to input
DapiSpecialCMDGetDirDX_8
This reads the direction of up to 64 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (8-bit wise). 1-bit represents 8 TTL inputs/outputs.
Description
This command reads the direction of up to 64 consecutive TTL inputs/outputs (8-bit wise).
1-bit represents 8 TTL inputs/outputs.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_DIR_DX_8, ULONG ch, ULONG dir, 0);
Parameter
handle = This is the handle of an open module
ch = Must always be 0!
dir = Must always be 0!
Return value
Direction status of 64 channels.
Bit 0: Direction of TTL 0-7 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 1: Direction of TTL 8-15 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 2: Direction of TTL 16-23 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 3: Direction of TTL 24-31 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 4: Direction of TTL 32-39 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 5: Direction of TTL 40-47 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 6: Direction of TTL 48-55 / 1=output, 0=input
Bit 7: Direction of TTL 56-63 / 1=output, 0=input
Remark
Only compatible with USB-TTL-32/64.
Programming example
ULONG ret = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_GET_DIR_DX_8, 0, 0, 0);
// Reads the direction of 64 channels
Watchdog functions
DapiWatchdogEnable
This function activates the watchdog.
Description
This function activates the watchdog.
Definition
void DapiWatchdogEnable(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiWatchdogEnable(handle);
//Activates the watchdog
DapiWatchdogDisable
This function deactivates the watchdog.
Description
This function deactivates the watchdog.
Definition
void DapiWatchdogDisable(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiWatchdogDisable(handle);
//Deactivates the watchdog
DapiWatchdogRetrigger
This function retriggers the watchdog timer.
Description
This function retriggers the watchdog timer.
Definition
void DapiWatchdogRetrigger(ULONG handle);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Return value
None
Programming example
DapiWatchdogRetrigger(handle);
//Retriggered the watchdog timer
Watchdog-Special
This function returns or sets various status information of the watchdog stick.
Description
This function returns or sets various status information of the watchdog stick.
Definition
ULONG DapiSpecialCommand(ULONG handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, cmd, par1, 0);
Parameter
handle=This is the handle of an open module
Querying the timeout relay counter
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_TIMEOUT_RELAIS_COUNTER_MSEC
par1=0
Query the watchdog status
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_STATUS
par1=0
Query the current timeout time
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_TIMEOUT_MSEC
par1=0
Query the watchdog timeout counter
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_WD_COUNTER_MSEC
par1=0
Set the time for how long relay 1 is switched
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_SET_TIMEOUT_REL1_COUNTER_MSEC
par1=Time for how long relay 1 is switched [ms]
Set the time for how long relay 2 is switched
cmd=DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_SET_TIMEOUT_REL2_COUNTER_MSEC
par1=Time for how long the 2nd relay is switched [ms]
Return value
Querying the timeout relay counter
return=Elapsed time after a timeout [ms]
Querying the watchdog status
return=Watchdog status
return=0 = Watchdog is deactivated
return=1 = Watchdog is activated
return=2 = Watchdog is retriggered
return=3 = Watchdog timeout
Query the current timeout time
return=Timeout time [ms]
Querying the watchdog timeout counter
return=Past time without retrigger [ms]
Programming example
return = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_TIMEOUT_RELAIS_COUNTER_MSEC, 0, 0);
//Querying the timeout relay counter
return = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_STATUS, 0, 0);
//Querying the watchdog status
return = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_TIMEOUT_MSEC, 0, 0);
//Query the currently used Timeout-Zeit
return = DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_GET_WD_COUNTER_MSEC, 0, 0);
//Querying the watchdog timeout counter
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_SET_TIMEOUT_REL1_COUNTER_MSEC, 500, 0);
//Switches the 1st relay after a timeout for 500 ms
DapiSpecialCommand(handle, DAPI_SPECIAL_CMD_WATCHDOG, DAPI_SPECIAL_WATCHDOG_SET_TIMEOUT_REL1_COUNTER_MSEC, 700, 0);
//Switches the 2nd relay after a timeout for 700 ms