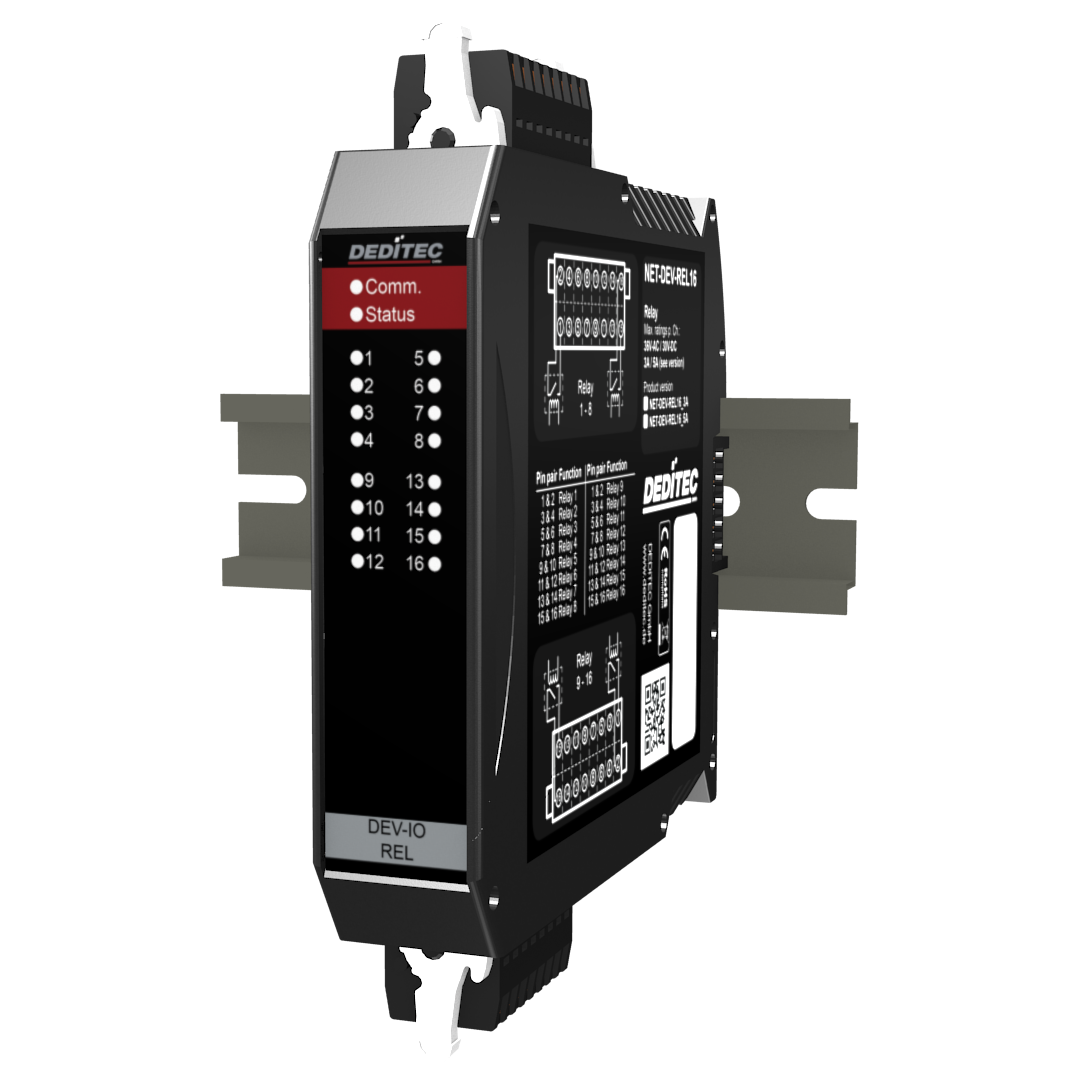
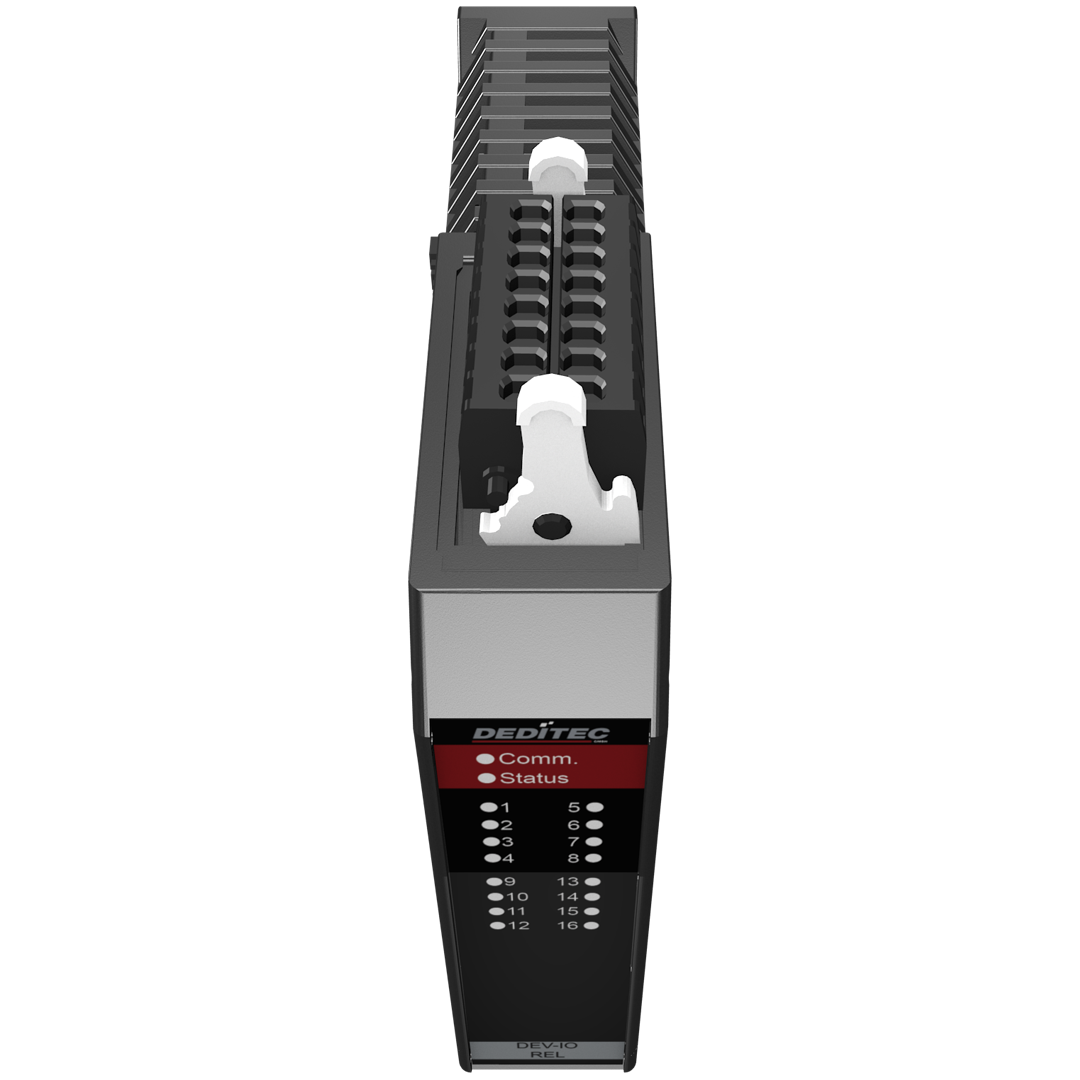
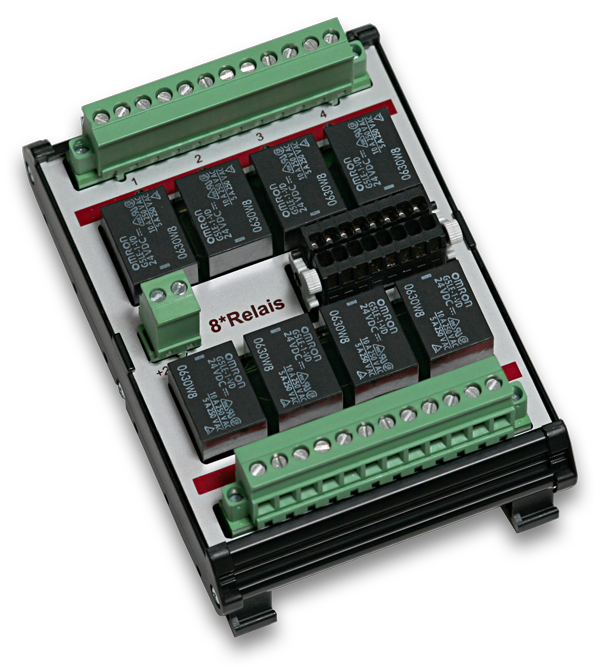
The NET-DEV-REL16_3/5A module has 16 digital outputs and is available with 3A or 5A switching capacity. It serves as an extension possibility for the NET-CPU basic modules and is integrated into an existing NET system by means of Plug’n Play plug connection (DIN Rail-Bus).
- 16 relay outputs (NO)
- Max. switching voltage: 48V AC / DC
- Max. switching current: 5A AC / DC
- Timer Function
- Timeout protection

Digital outputs
Relay 3A / 5A
Power relays with normally open (NO) function are used as digital output. They are suitable for switching capacities up to 5A and have a life time of up to 10 million switching cycles. The galvanic separation between input and output circuit is up to 3kV.
Timer Function
All digital outputs of the NET series have a timer function. This allows the outputs to be switched on and off automatically for a freely definable period of time. Even if the connection to the control PC is interrupted.

Fail-safe mode
The fail-safe mode is a safety function in which the DEDITEC module switches to a previously configured, safe switching state in the event of a connection failure.
This is intended to prevent connected installations or systems from continuing to run in an uncontrolled manner.
Three switching states can be defined for each digital output: a) Switched off, b) Switched on or c) Unchanged.
The fail-safe circuit is triggered by a timeout protection function. If the control unit no longer receives any commands from the control PC within a previously defined period of time, the timeout function comes into effect. The cause of a timeout can be a loss of connection between the control PC and the DEDITEC control system or failure of the control PC.
Timeout modes
Three timeout modes are available:
A) “Normal mode” is valid once and must be reactivated manually by software command after each timeout event. The customer application still has access to all controller outputs.
B) In “Auto reactivate mode”, the timeout function is automatically reactivated after communication with the control PC has been re-established. The customer application still has access to all outputs of the control unit.
C) The “Secure outputs mode” blocks access to the outputs after the timeout event. Unlocking can only be carried out by software command. This is an important safety aspect

Easy installation thanks to DIN rail bus
Thanks to the practical NET-Bus connector, which is clipped into the top-hat rail, individual modules of a system can be added or exchanged very easily. This Plug’n Play principle makes commissioning easier and eliminates the need for tiresome wiring.

LEDs
On the front side of our NET modules there are a number of status LEDs. These give you a quick overview of the most important functions of the modules, such as the switching states of the individual I/Os, module status or whether clean communication via the DIN rail bus is possible. This can be very helpful for fast error analysis, especially for field applications.